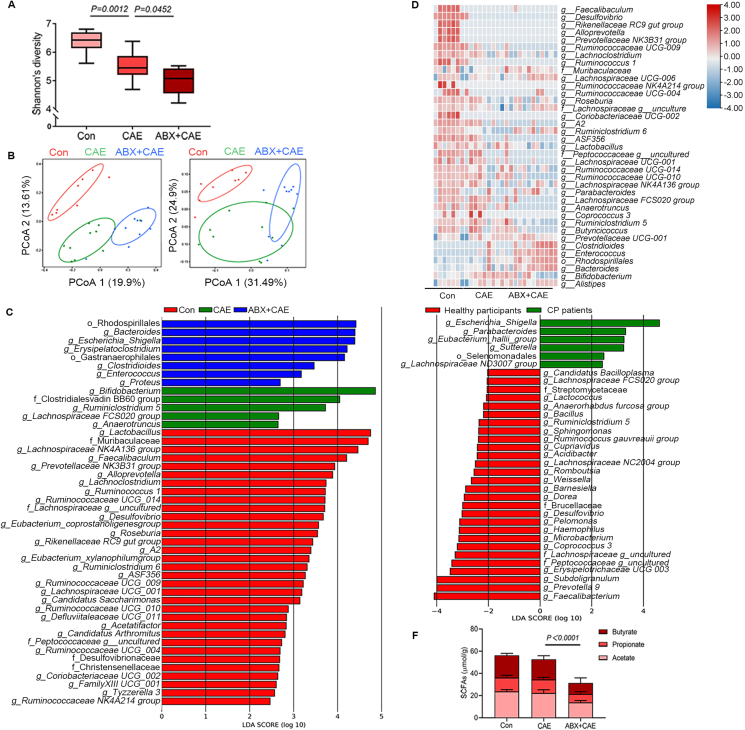
Figure 1.
A broad-spectrum antibiotic (ABX) cocktail intensifies gut dysbiosis and reduction of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-producing bacteria in chronic pancreatitis (CP). (A) The diversity shown by Shannon's index (Con, n = 8; CAE, n = 10; ABX + CAE, n = 10). (B) Principal coordinates analysis comparing the microbiome composition in colon content of mice (Con, n = 8; CAE, n = 10; ABX + CAE, n = 10; left: unweighted, right: weighted). (C) The LEfSe analyses of microbiome composition (based on abundance) distribution of three groups of mice, histogram of the LDA scores reveals the most differentially abundant taxa among different treatments (Con, n = 8; CAE, n = 10; ABX + CAE, n = 10). (D) Heatmap representation of SCFAs-producing bacteria (based on absolute count) in three groups of mice (Con, n = 8; CAE, n = 10; ABX + CAE, n = 10). (E) The LEfSe analyses of microbiome composition distribution of healthy participants and CP patients (healthy participants, n = 69; CP patients, n = 71). (F) The levels of SCFAs (acetate, propionate and butyrate) in colon content (n = 6). Data (A) were representative and were the min to the max from three independent experiments. Data (F) are representative and were the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments. P values were calculated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's post hoc test for multiple comparisons.