Figure 8. H2B loss during Caenorhabditis elegans epidermal development.
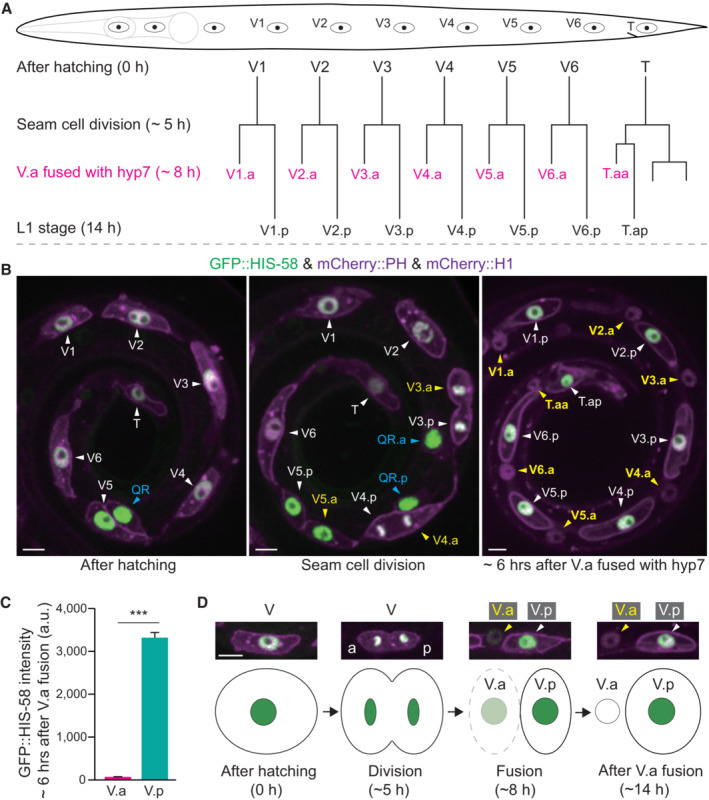
- Seam cell (V) lineages in well‐fed C. elegans L1 larvae. A seam cell (V) divides to generate the anterior daughter cell (V.a) and the posterior daughter (V.p). V.a cells fuse with the epithelial hyp 7 syncytium, whereas V.p cells do not fuse and keep dividing in the following larval stages.
- Fluorescence images of seam cells. The GFP::HIS‐58 (H2B) was expressed under the control of the seam cell‐specific wrt‐2 promoter, and the mCherry::PH (membrane) and mCherry::HIS‐24 (H1, nucleus) were expressed under the control of another seam cell‐specific ceh‐16 promoter. The white arrowheads indicate the seam cell V or V.p nuclei, whereas the yellow arrowheads indicate V.a nuclei. The blue arrowheads indicate the Q cells. Because the Q cell and V5 seam cell are produced by the same mother epidermal cell, wrt‐2 and ceh‐16 promoters are expressed in Q cells. The right image shows that V.p (white arrowheads and cell names) maintained GFP::H2B fluorescence, but V.a lost the GFP signal (yellow arrowheads and cell names) 6 h after V.a fused with hyp 7. Scale bar, 5 μm.
- Quantification of GFP::HIS‐58 in the seam cell nuclei (n = 48) and hyp 7 cell nuclei (n = 48) after the seam cell V.a fused with hyp 7 in L1 larvae. Data shown are means ± SEM; P values were determined by a two‐tailed unpaired t‐test, ***P < 0.001.
- Representative images and schematics of H2B loss after seam cells fused with hyp 7. a, anterior; p, posterior. Scale bar, 5 μm.
Source data are available online for this figure.
