Figure 2.
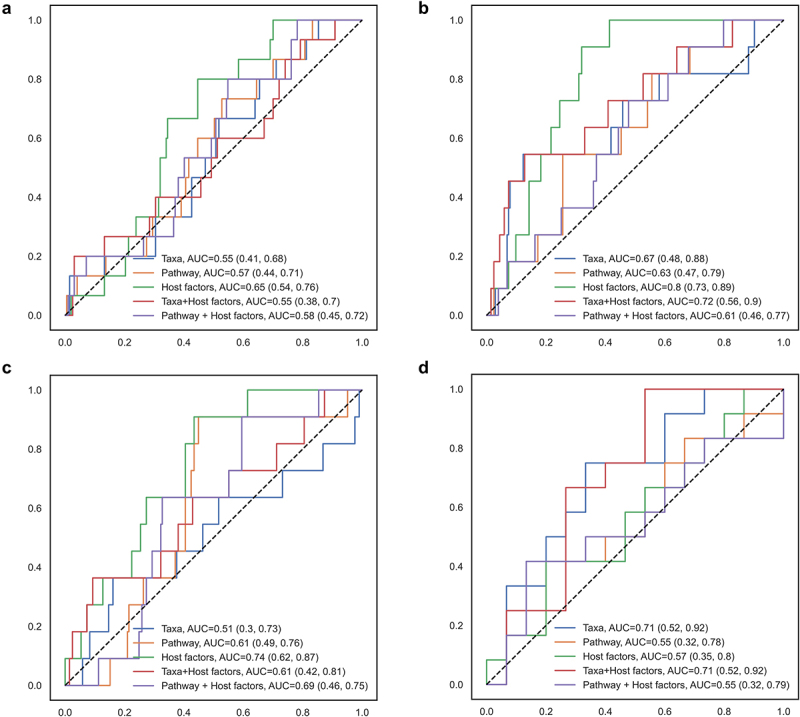
Random forest model classifying IBS subtypes according to gut microbial taxa, functional pathways, and host factors.
(a) IBS-C, (b) IBS-D, and (c) IBS-M were distinguished from non-IBS group and (d) IBS-C was distinguished from IBS-D. A 5-fold cross validation approach was implemented, and the area under the curve (AUC) and 95% confidence intervals were estimated based on a 75/25 random split of training and testing datasets, with 9999 resampling for the bootstrap distribution. A total of 768 taxa, 445 pathways, and 11 host factors (sex, age, education, smoking, menopausal status, hormone therapy, antibiotic use, probiotic use, BMI, diet quality, and total energy intake) were included.
