Figure 3.
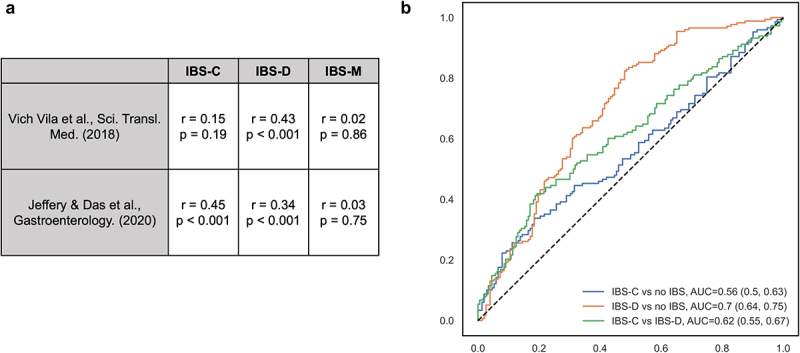
Taxonomic-level results were comparable with prior studies.
(a) The correlation between parameter estimates for specific taxa-IBS associations between our study, Vich Vila et al.8 (results for IBS defined using self-reported Rome III questionnaire), and Jeffery and Das et al.13 (clinically identified IBS using Rome IV criteria) were assessed using Pearson correlation. (b) A cross prediction using random forest classification built upon our dataset (367 overlapping taxa) to distinguish IBS subgroups in Mars et al.9
