Figure 5.
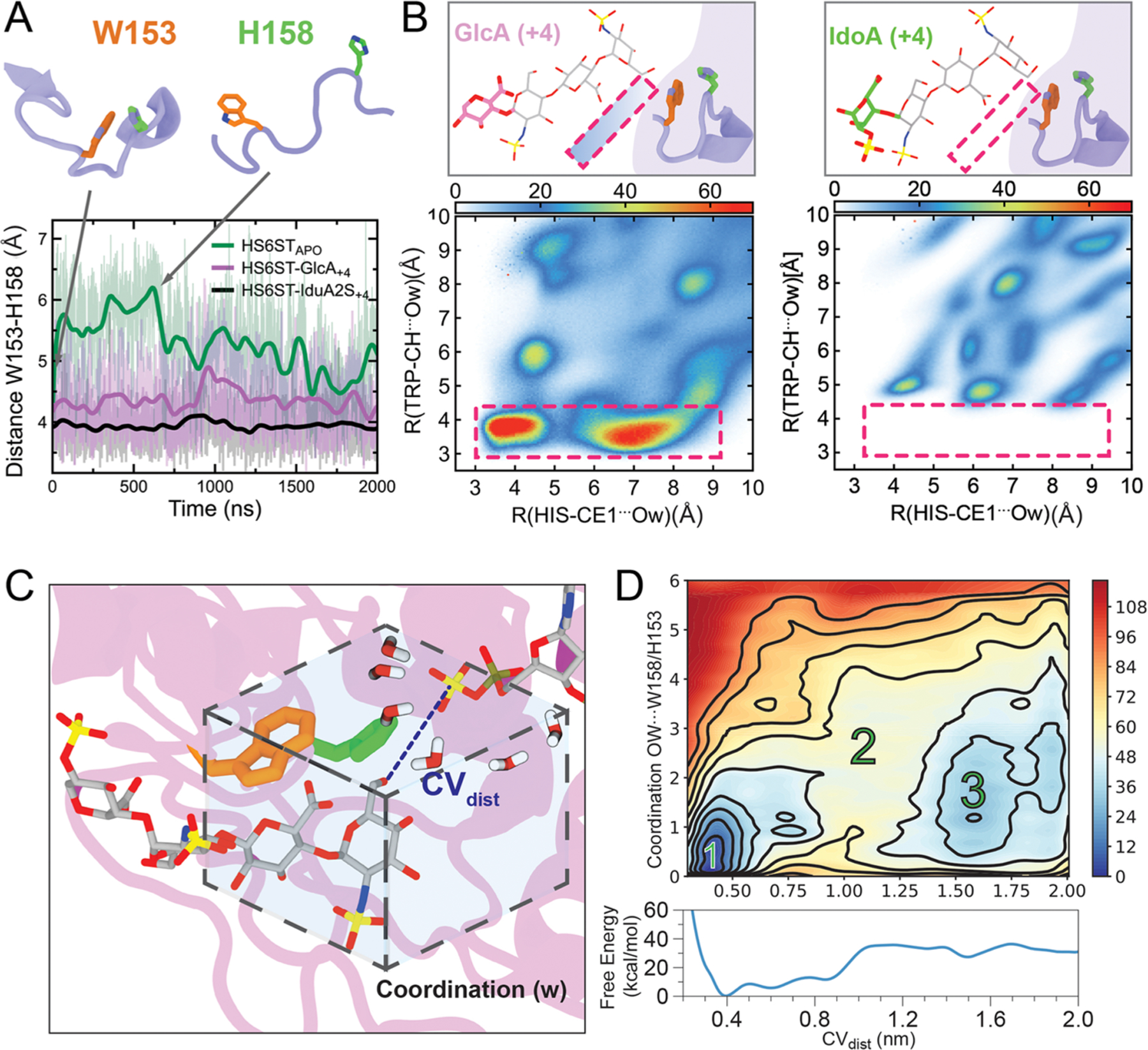
HS6ST substrate at position +4 influences HS6ST motility and active site hydration. (A) Distances between W153 and H158 during HS6ST simulations. (B) 2D-radial distribution functions (2D-RDF) function for the two closest atoms from W153 and H158 for both HS6ST:IdoA2S+4 and HS6ST:GlcA+4 simulations. Pink dashed lines outline the two water clusters observed in HS6ST:GlcA+4 simulations. Atoms are labeled according to AMBER force field nomenclature. (C) Diagrams of coordination parameters defined for free energy calculations of active site hydration and acceptor coupling. The dashed box displays the coordination of waters surrounding the active site collective variable parameter (w). The substrate is shown as gray sticks. (D) Projection of the FES onto CVdist and CVw, as well as onto CVdist alone (bottom). Numbers indicate the most relevant metastable states 1 and 3, separated by a high-energy barrier, 2. Contours are drawn every 12 kcal/mol.
