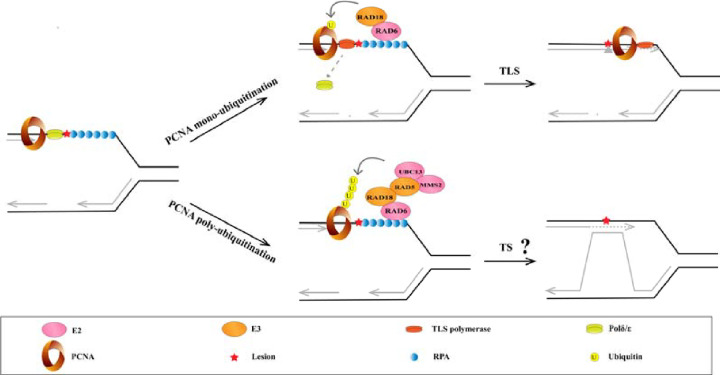
Figure 3. PCNA ubiquitination in the translesion synthesis and template switching pathways.
PCNA monoubiquitination promotes polymerase switching to activate the translesion synthesis pathway (TLS) and enable the bypassing of problematic lesions. Under replication stress, RPA-coated ssDNA recruits a complex of RAD18 and RAD6, leading to PCNA monoubiquitination at K164. This modification disrupts the affinity of PCNA for B-family DNA polymerases (Polδ and Polε) and increases its affinity for specialized Y-family polymerases (including Polη, Polι, Polκ, and Rev1); these events lead to error-prone TLS. In template switching (TS), following the initial RAD6/RAD18-dependent monoubiquitination of PCNA at K164, UBC13-MMS2, and RAD5 are required to generate K63-linked polyubiquitin chains. However, the exact details of TS following PCNA polyubiquitination remain unknown.