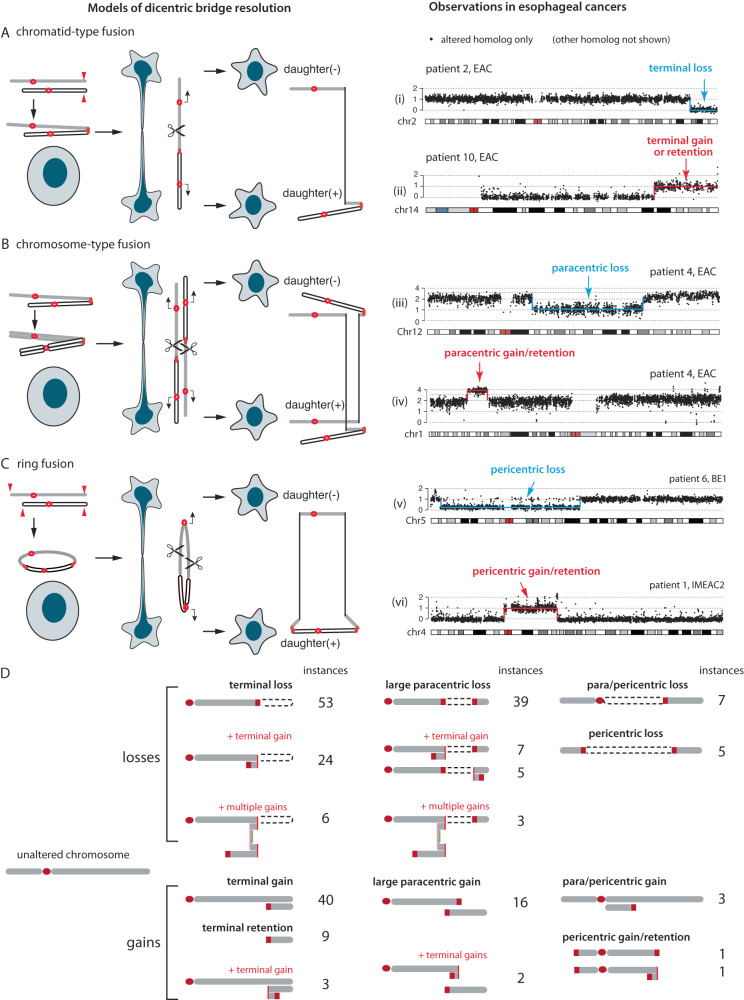
Fig. 5. Segmental copy-number alterations in BE/EAC genomes that match the outcomes of dicentric chromosome bridge resolution.
A–C (Left) Different types of dicentric chromosome breakage and their copy-number outcomes: (A) terminal; (B) paracentric; or (C) pericentric segmental copy number changes. The open and filled chromatids may be sister chromatids or different chromosomes. Both A and B were demonstrated in vitro in ref. 38. The model that pericentric copy-number changes may arise from broken dicentric ring chromosomes (C) or multicentric chromosomes (when the p- and q-termini of a chromosome are fused to two other chromosomes) has not been demonstrated in vitro but is plausible as telomere crisis can lead to multiple shortened telomeres that generate dicentric rings. (Right) Examples of SCNAs in BE/EAC genomes that recapitulate the predicted SCNA outcomes of bridge resolution. The allelic copy-number plots (25 kb bins) show the DNA copy number of the altered chromosome; the intact homolog is not shown. Examples of gain and loss in each group are unrelated. See “Online Data” for the copy-number plots of both homologs in each sample. D Summary of terminal/internal SCNAs in BE/EAC genomes, including copy-number patterns consistent with different combinations of successive BFB cycles with SCNA outcomes shown in A–C. Numbers denote instances of each pattern. See Supplementary Data 5 for the complete list.