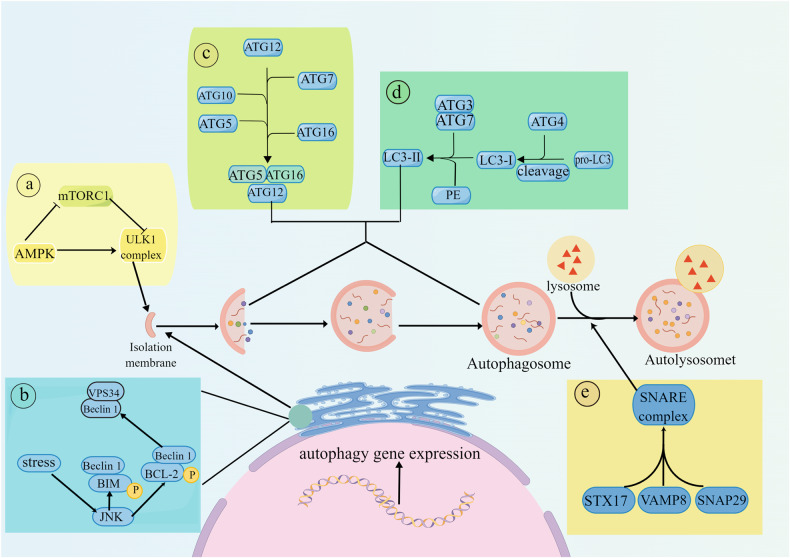
Fig. 1. Mechanism of autophagy.
Autophagy is a complex self-degradation process involving the following key steps: ①Signaling pathways regulate the initiation of autophagy. AMPK inhibits the formation of the mTORC1 complex, which weakens the inhibitory effect of mTORC1 on the formation of the ULK1 complex, thereby promoting the production of autophagic vesicles. ② The Beclin-1/VPS34 complex promotes the extension of autophagic vesicles. The activated kinase JNK destroys the Beclin1/BCL-2 and Beclin1/BIM complexes by phosphorylating BCL-2 and BIM to free Beclin1. Free Beclin1 activates VPS34 and binds to it to form a complex, and the PI3P that is produced promotes the extension of autophagic vesicles. ③ The ATG12-ATG5 complex binds to ATG16 and completes polymerization. The polymer complex ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L is formed by a series of ATG5, ATG12 and ATG16L actions, and then, the polymer complex is fused with autophagic vesicles. ④ LC3 is inserted into autophagosomes through a series of reactions. The cysteine protease ATG4 cleaves LC3 into LC3-I, which is then processed by ATG3, ATG7 and phosphatidylethanolamine to form LC3-II. Subsequently, LC3-II is inserted into the autophagosomes. ⑤ Autophagosomes and lysosomes fuse to form autolysosomes. STX17 binds to SNAP29 and VAMP8 to form a SNARE complex that is transferred to the autophagosomal membrane, allowing lysosomes to fuse with autophagosomes and form autolysosomes. The graph was drawn with Figdraw.