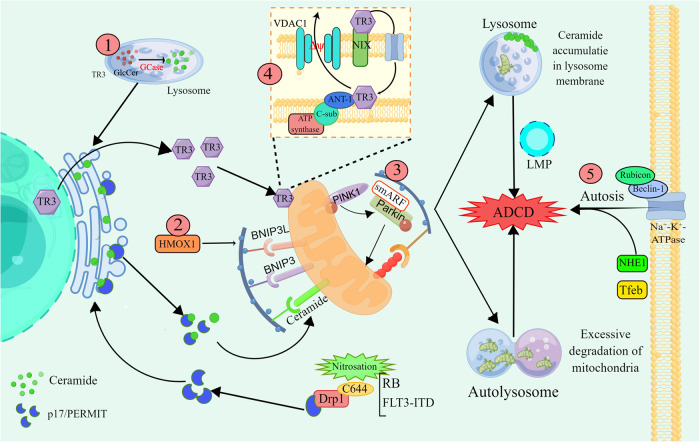
Fig. 3. Mechanisms underlying lethal mitophagy and autosis.
① GCase overexpression promotes lysosomal glucose ceramide catabolism into glucose and lysosomal ceramide, which are recycled in the ER. Under conditions of RB or FLT3-ITD inhibition, Drp1 C644 nitrosylation leads to the release of the transport protein p17/PERMIT. Ceramide is transported from the ER to mitochondria by p17/PERMIT, which functions as a mitophagy receptor, and its binding to lipidated LC3 promotes lethal mitophagy. In addition, ceramide or dihydroceramide accumulates in autophagosomal membranes to trigger LMP. ②AT-101 induces the transcription and translation of HMOX1, BNIP3L and BNIP3 and promotes excessive mitophagy. ③smARF promotes excessive mitophagy by binding to Parkin. ④ TR3 is translocated from the nucleus to mitochondria, interacts with NIX and enters the mitochondrial membrane space via Tom40 and Tom70. TR3 interacts directly with ANT-1 and promotes VDAC1 action to alter the MMP and thus induce mitophagy. ⑤ Rubicon and Beclin-1 bind directly to Na+-K+-ATPase to promote autosis. This graph was drawn with Figdraw.