Figure 4.
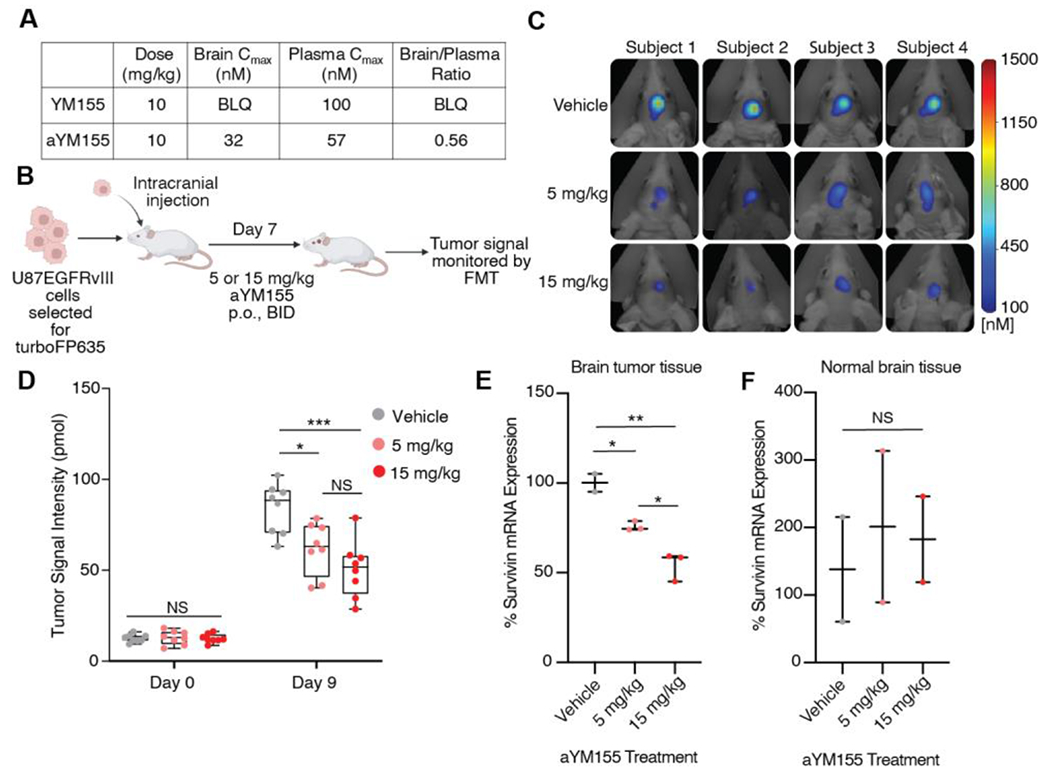
aYM155 penetrates the brain and reduces GBM tumor growth in an intracranial xenograft model. (A) Mouse tissue distribution properties of aYM155 (10 mg/kg, P.O.). (B) Schematic of GBM orthotopic intracranial xenograft model. U87EGFRvIII cells, engineered to carry turboFP635, were intracranially injected into six-week-old female athymic nude mice (n = 8 for each group). aYM155 was administered 7 days post injection. Created with Biorender.com. (C) Representative FMT tumor images of mice at day 9 of aYM155 dosing. (D) Tumor growth curves for mice treated with vehicle, 5 mg/kg, or 15 mg/kg aYM155 administered orally twice daily (n=8 mice per group). (E) qRT-PCR analysis of mouse brain tumor tissue. Student’s t-test was used to assess significance. Each data point represents the mean of 3 technical replicates per mouse (n = 2 mice for vehicle, n = 3 mice for 5 and 15 mg/kg). (F) qRT-PCR analysis of normal mouse brain tissue. Each data point represents the mean of 3 technical replicates per mouse (n = 2 mice). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. NS = not significant.
