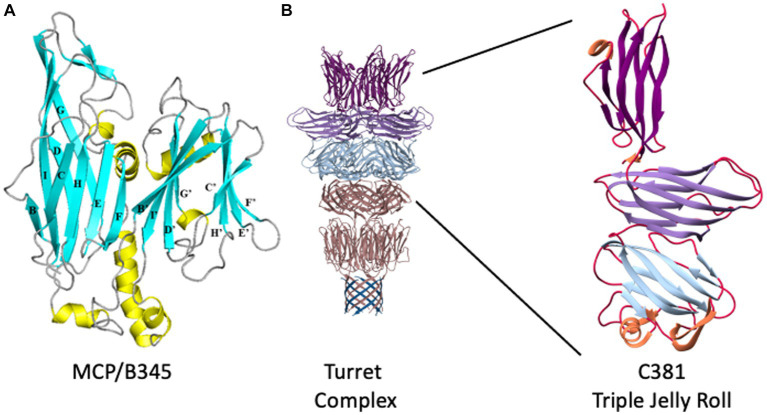
Figure 2.
STIV structural proteins. (A) Ribbon representation of B345, the major capsid protein of STIV. β-strands are depicted in cyan, α-helices in yellow, loops in gray. The structure is composed of two domains, an N-terminal domain (left) and a C-terminal domain (right). Each domain adopts the jelly roll fold, which is composed of two four-stranded β-sheets. In the N-terminal domain, the first sheet is formed of strands B, I, D and G (BIDG) at the back of the structure, and the second sheet of strands C, H, E and F (CHEF) at the front of the structure. The two β-sheets pack against each other to form a β-sandwich. Similarly, the C-terminal jelly roll is composed of strands B′, I′, D′, and G’ in the B’I’D’G’ sheet, and strands C′, H′ E’, and F′ in the C’H’E’F′ sheet. Adapted from Khayat et al. (2005). (B) The structure of the STIV turret. β-strands emanating from the A55 membrane anchor are at the bottom, in blue, where they interdigitate with the N terminus of A223 to form a ten-stranded hemolysin-like β-barrel. The two-domain, double jelly roll structure of A223 is shown above that in pink, followed by the three-domain jelly roll structure of C381 in light blue, light purple, and dark purple at the top. To the right, an enlarged view of a single C381 protomer. The N-terminal jelly roll is at the bottom, the C-terminal jelly roll domain at the top. Adapted from Hartman et al. (2019).