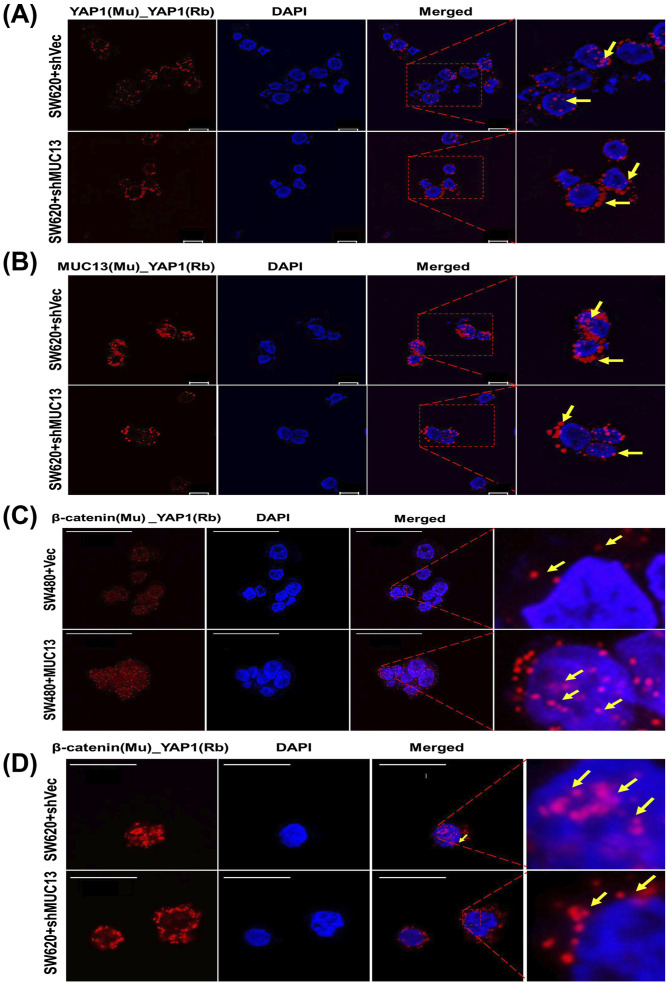
Figure 5. MUC13 facilitates nuclear translocation of YAP1/β-catenin survival complex PLA was performed on pelleted, cryofixed, cryosection cells using the indicated anti-mouse (MAb) and anti-rabbit (PAb) antibodies and PLA probes.
Red dots indicated by yellow arrows represent the physical interaction among listed proteins in used cell lines. (A) PLA analysis of YAP1 in MUC13 knockdown cells (SW620+shMUC13), leading to decreased nuclear localization of YAP1 compared with the ShCtrl cells (scale bar, 10 μm). (B) PLA analysis of MUC13 and YAP1 in MUC13 knockdown cells (SW620+shMUC13) showed increased localization to the perinucleus compared with vector control (scale bar, 10 μm). (C) Confocal images show higher YAP1/β-catenin survival complexes in MUC13 overexpression (SW480+MUC13) cells compared to vector only. Most of the YAP1/β-catenin complexes are translocated to the nucleus (scale bar, 50 μm). (D) Knockdown of MUC13 prevented the nuclear translocation of the YAP1/β-catenin complex as it was predominantly localized outside the nuclear envelope in SW620+shMUC13 cells (scale bar, 20 μm). The images depict at least three independent experiments.