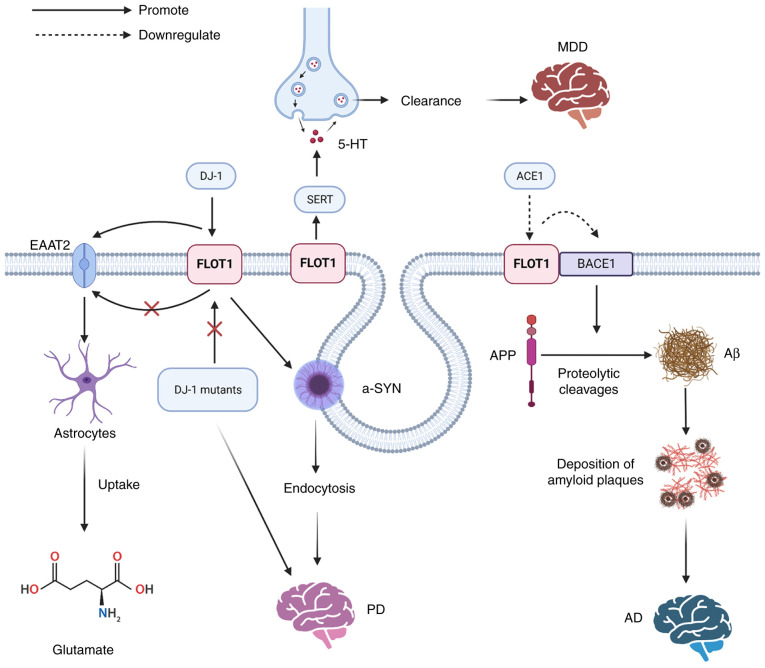
Figure 4.
The mechanisms of FLOT1 leading to neurological diseases: Aβ is produced by proteolytic cleavages of APP under the influence of BACE1, the accumulation of which can lead to the development of AD, and the overexpression of FLOT1 suppresses the activity of BACE1. DJ-1 can regulate the protein stability of FLOT1, but the PD-associated DJ-1 mutants fail to regulate the FLOT1. DJ-1 promotes the expression of EAAT2 by upregulating FLOT1, promoting the uptake of glutamate by astrocytes. FLOT1 contributes to the microdomain localization and regulation of SERT, and SERT can control the reuptake of released 5-HT from the synaptic cleft into the presynaptic terminal to regulate 5-HT clearance, leading to the development of MDD. Aβ, amyloid-β peptide; APP, amyloid precursor protein; BACE1, β-site APP cleaving enzyme 1; AD, Alzheimer's disease; PD, Parkinson's disease; FLOT, flotillin protein; DJ-1, PD protein 7; EAAT2, glial glutamate transporter; SERT, presynaptic high-affinity 5-HT transporter; MDD, major depressive disorder; EAAT2, glial glutamate transporter; ACE1, angiotensin-converting enzyme 1; -SYN, α-synuclein.