Figure 1.
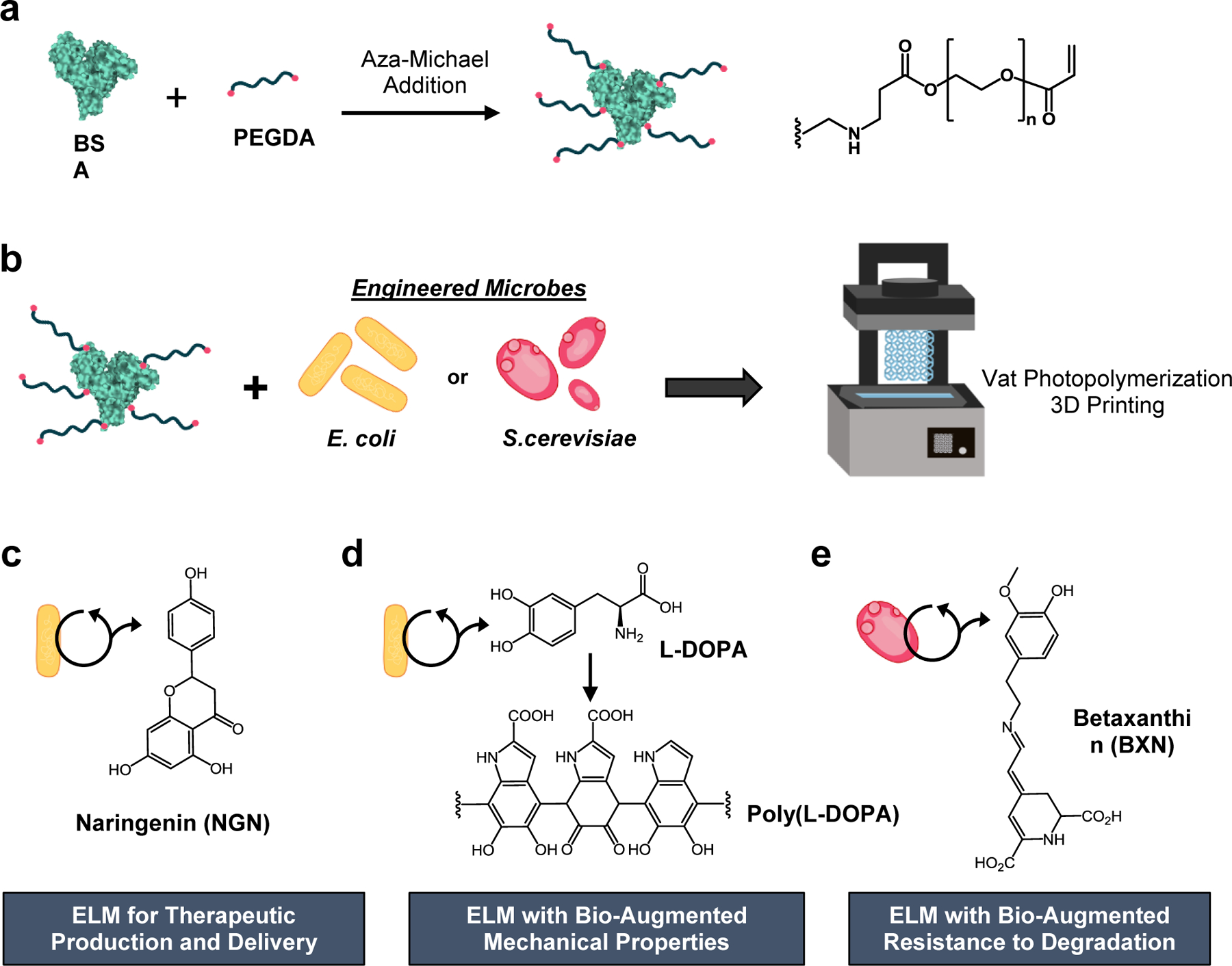
Additive manufacturing of ELMs with bio-augmented functionality and mechanical properties. a) BSA was functionalized via aza-Michael addition to afford pendant PEG-acrylate groups. b) Engineered E. coli or S. cerevisiae was added to the PEG-functionalized BSA to create an aqueous based resin for vat photopolymerization. The microbes were entrapped within the polymerized BSA-PEGDA hydrogel network. E. coli were engineered to produce c) naringenin or d) L-DOPA (the L-DOPA polymerized to afford poly(L-DOPA), and e) S. cerevisiae was engineered to produce betaxanthins. The 3D printed ELMs are referred to as ELM-EC-NGN, ELM-EC-LDOPA, or ELM-SC-BXN, respectively. (EC = E. coli, SC = S. cerevisiae, LDOPA = L-DOPA, BXN = betaxanthins, and NGN = naringenin).
