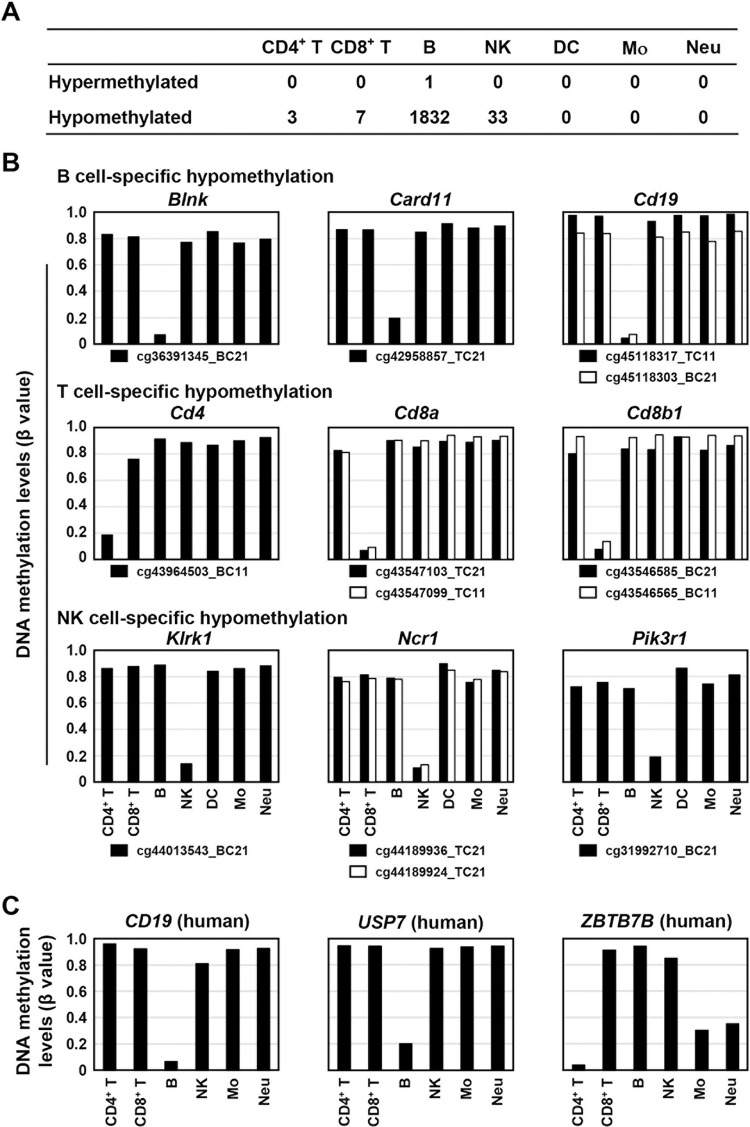
Fig 3. Cell type-specific hypomethylation of genes involved in lineage commitment.
(A) Number of CpG sites hypermethylated or hypomethylated in one cell type of leukocytes. One CpG site was specifically hypermethylated in B cells, and three, seven, 182, and 33 CpG sites were specifically hypomethylated in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, B cells, and NK cells, respectively. (B) Lineage-specific hypomethylation of CpG sites within genes related to specific types of leukocytes. CpG sites within genes involved in B cell function, Blnk, Card11, and Cd19, were specifically hypomethylated in B cells. CpG sites within genes involved in T cell function, Cd4a, Cd8a, and Cd8b, were specifically hypomethylated in T cells. CpG sites within genes involved in NK cell function, Klrk1, Ncr1, and Pik3r1, were specifically hypomethylated in NK cells. (C) Human relevance of lineage-specific hypomethylation. The leukocyte cell type-specific hypomethylation of Cd19, Usp7, and Zbtb7b in the mouse genome was conserved at their homologous regions in the human genome.