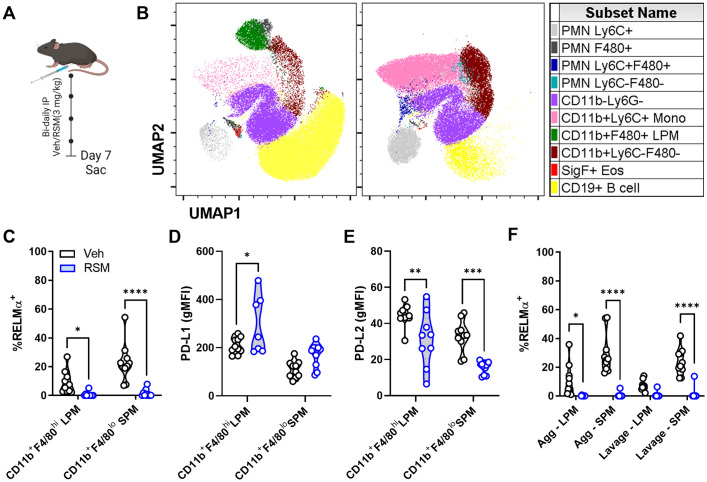
Fig 5. In vivo choline kinase inhibition remodels peritoneal cell populations and impairs RELMα expression.
A) Schematic of 7-day in vivo choline kinase inhibition. Mice were treated intraperitoneally with vehicle (40% DMSO in PBS) or RSM-932a (3 mg/kg) every other day for 6 days and sacrificed on day 7. B) UMAP of peritoneal cell populations. n = 9–10, representing 2 independent experiments. C) Intracellular RELMα expression in live CD11b+F4/80hi large (LPM) and CD11b+F4/80lo small (SPM) peritoneal macrophages. Two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s test for multiple comparisons (* p < 0.05, **** p < 0.001). D-E) PD-L1 or PD-L2 expression (gMFI) in live CD11b+F4/80hi LPM and CD11b+F4/80lo SPM. Two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s test for multiple comparisons (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). F) Intracellular RELMα expression in LPM and SPM isolated from peritoneal cavity aggregates or suspended lavage cells. Two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s test for multiple comparisons (* p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001). Schematics were created using BioRender.