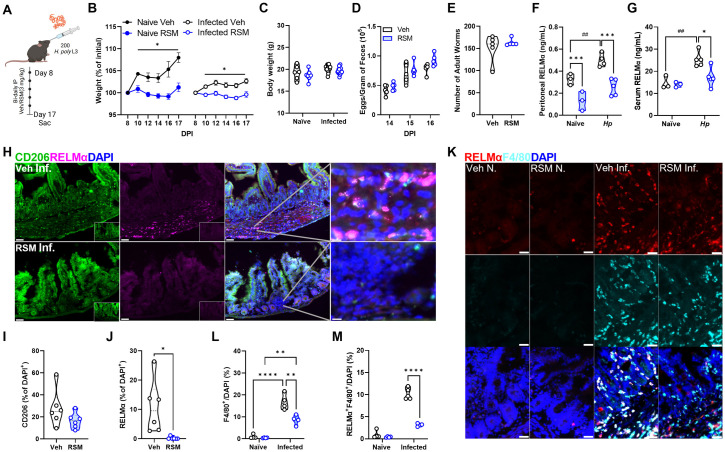
Fig 7. In vivo choline kinase inhibition during primary infection impairs systemic and intestinal RELMα and intestinal macrophage alternative activation.
A) Schematic of primary infection with 200 H. polygyrus (Hp) L3 larvae through oral gavage. Mice were treated intraperitoneally with vehicle (40% DMSO in PBS) or RSM-932a (3 mg/kg) every other day for 8 days starting on day 8 and sacrificed on day 17. B-C) Percentage of weights at start of vehicle or RSM injections at 8 DPI with H. polygyrus (B) or final weights at day 17 (C). Mixed-effects analysis with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons (* p < 0.05). D-E) Eggs in feces were counted at multiple time points after infection, and E) adult worms were isolated from the small intestine and enumerated on the day of sacrifice. Values represent means ± SEM (n = 3–5 mice per group), representative of 3 experiments. Two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s test for multiple comparisons and unpaired t test (ns). F-G) Detection of serum and G) peritoneal fluid RELMα by ELISA in naïve and H. polygyrus-infected mice. n = 3–5 per group. Two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s test for multiple comparisons (* p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 for differences between treatment and ## p < 0.01 for differences between naïve and infected vehicle-treated mice). H-L) Immunofluorescent staining of intestinal tissue for CD206 and RELMα against DAPI counterstain. Scale bar 50 μm. Quantification of CD206+ (I) or RELMα+ (J) per DAPI+ cell. Unpaired t test (* p < 0.05). Quantification of F4/80+ (K) and RELMα+F4/80+ (L) per DAPI+ cell. n = 6. Two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s test for multiple comparisons (**** p < 0.0001). Schematics were created using BioRender.