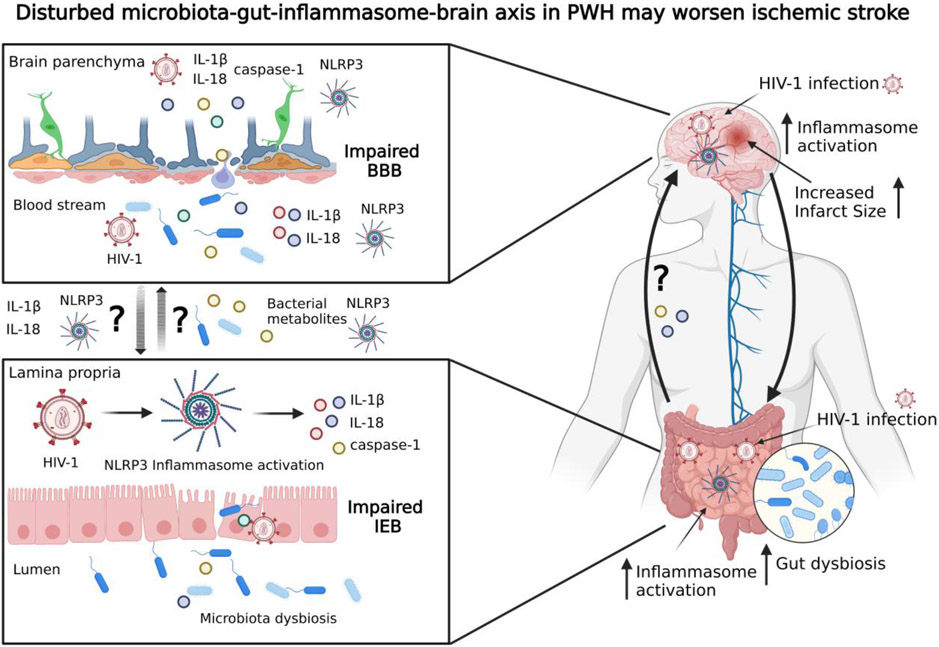
Figure 6, Key Figure. Dysregulation of the microbiota-gut-inflammasome-brain axis in HIV-1 infection may worsen ischemic stroke.
HIV-1 can infect both the CNS and the gut, activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, and induce dysregulation of the gut microbiota. Gut dysbiosis also induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation through a positive feedback loop. Some of the effector mediators of NLRP3 inflammasome activation are IL-1β, IL-18 and caspase-1, whose release may lead to impairments of the intestinal epithelial barrier. Bacterial metabolites and proinflammatory cytokines can travel from the gut to the brain via the gut-brain axis, where they may increase NLRP3 inflammasome activation and BBB damage. It has been proposed that activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and enhanced inflammatory responses are important mechanisms contributing to worsening of ischemic stroke outcomes and post-stroke recovery in PWH. BBB, blood-brain barrier; IEB, intestinal epithelium barrier. Figure created with BioRender (www.BioRender.com).