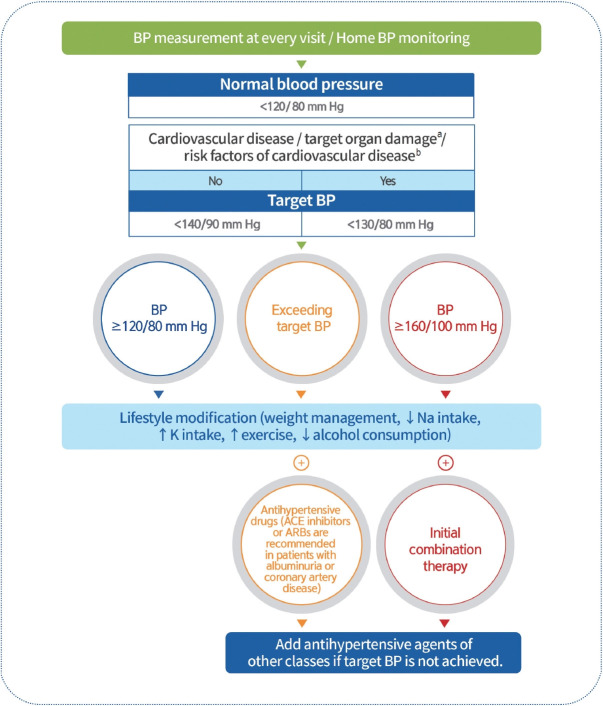
Fig. 2.
Hypertension management in patients with diabetes. Blood pressure (BP) should be measured at every clinic visit, and home BP monitoring is recommended. The recommended target BP level is <140/90 mm Hg in adults with diabetes without cardiovascular disease (CVD) or associated risk factors. The recommended target BP is <130/80 mm Hg in diabetic adults with CVD, target organ damage (albuminuria, chronic kidney disease, retinopathy, and left ventricular hypertrophy), or risk factors for CVD. Adults with diabetes and a BP >120/80 mm Hg should undergo lifestyle modifications. Pharmacological therapy should be implemented if the target BP is not achieved. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are preferred when accompanied with albuminuria or coronary artery disease. If the BP exceeds 160/100 mm Hg, initial combination therapy is recommended. If BP is not controlled by primary antihypertensive medications, combination therapy using other drugs with different mechanisms is recommended. aAlbuminuria, chronic kidney disease, retinopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, bAge (men ≥45 years, women ≥55 years), smoking, obesity, dyslipidemia, family history of early-onset coronary heart disease.