Fig. 4.
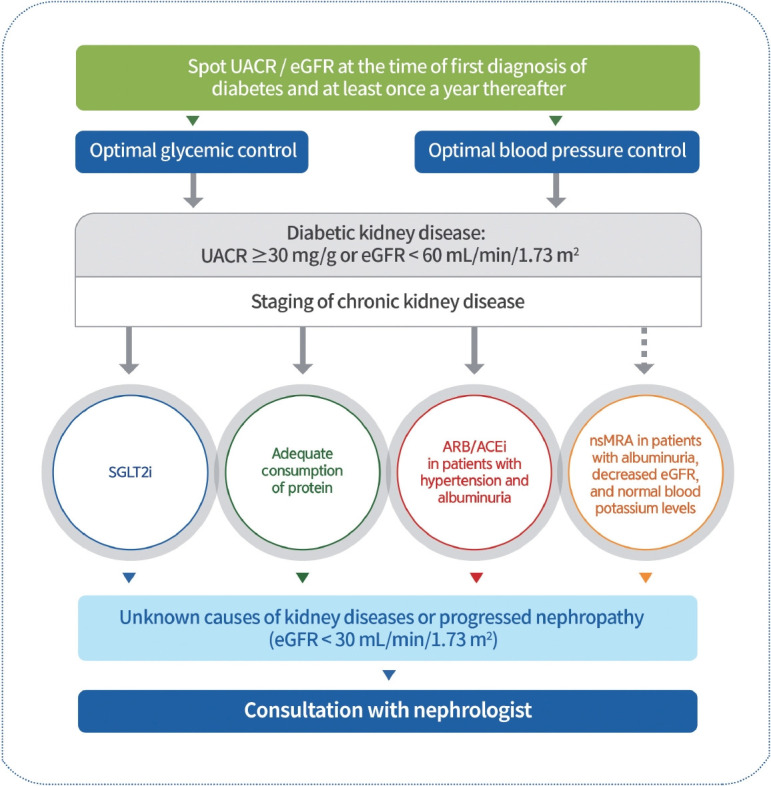
Management of diabetic kidney disease. Urine albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) should be evaluated in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) at the time of diagnosis and at least once yearly. Therefore, blood glucose levels and blood pressure should be optimally controlled. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) that have shown renal benefits should first be used to inhibit diabetic kidney disease (DKD) progression in patients with albuminuria or a reduced eGFR. DKD patients consume adequate protein amounts. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEis) or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) should be prescribed for patients with diabetes, hypertension, and albuminuria. Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (nsMRAs), such as finerenone, which has shown cardiac and renal benefits, can be considered in patients with T2DM with albuminuria, decreased eGFR, and normal blood potassium levels. Request consultation with nephrologists for those with unknown causes of kidney disease or progressive nephropathy.
