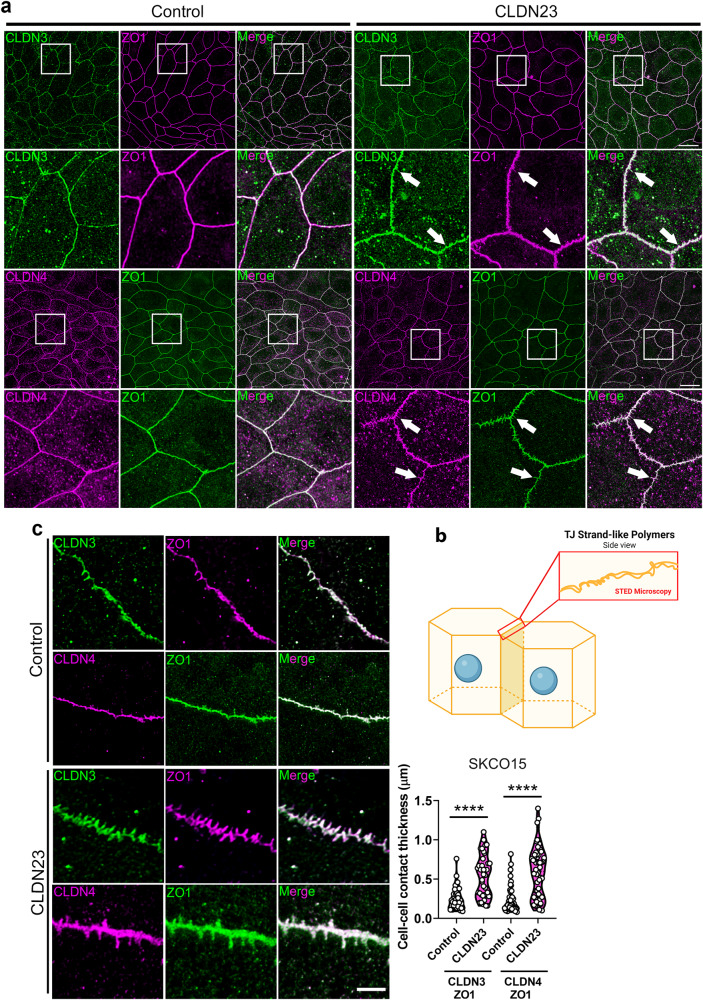
Fig. 4. CLDN23 influences the TJ morphology of intestinal epithelial cells.
a Immunofluorescence staining and representative deconvoluted confocal images of control SKCO15 and CLDN23 overexpressing SKCO15 monolayers stained with anti-ZO1 (magenta & green) and either anti-CLDN3 (green), or anti-CLDN4 (magenta) antibodies. Scale bar: 20μm. Arrows point to TJ spike formation along cell-cell contacts. b Schematic representing the visualization of TJ strand formation employing super-resolution STED microscopy. Created with BioRender.com. c Left, representative super-resolution STED microscopy images in control SKCO15 IECs and CLDN23 overexpressing SKCO15 IEC monolayers stained with anti-ZO1 (magenta or green) and either anti-CLDN3 (green), or anti-CLDN4 (magenta) antibodies. Scale bar: 20 μm. Right, histograms showing cell–cell contact thickness. Results show the mean ± SD of two independent experiments. A total of 33 (CLDN3/ZO1) and 50 (CLDN4/ZO1) cell-cell contacts were analyzed for control cells, while 38 (CLDN3/ZO1) and 55 (CLDN4/ZO1) were analyzed for CLDN23 overexpressing cells. ****p < 0.0001; statistical analysis was done with two-tailed Student’s t test.