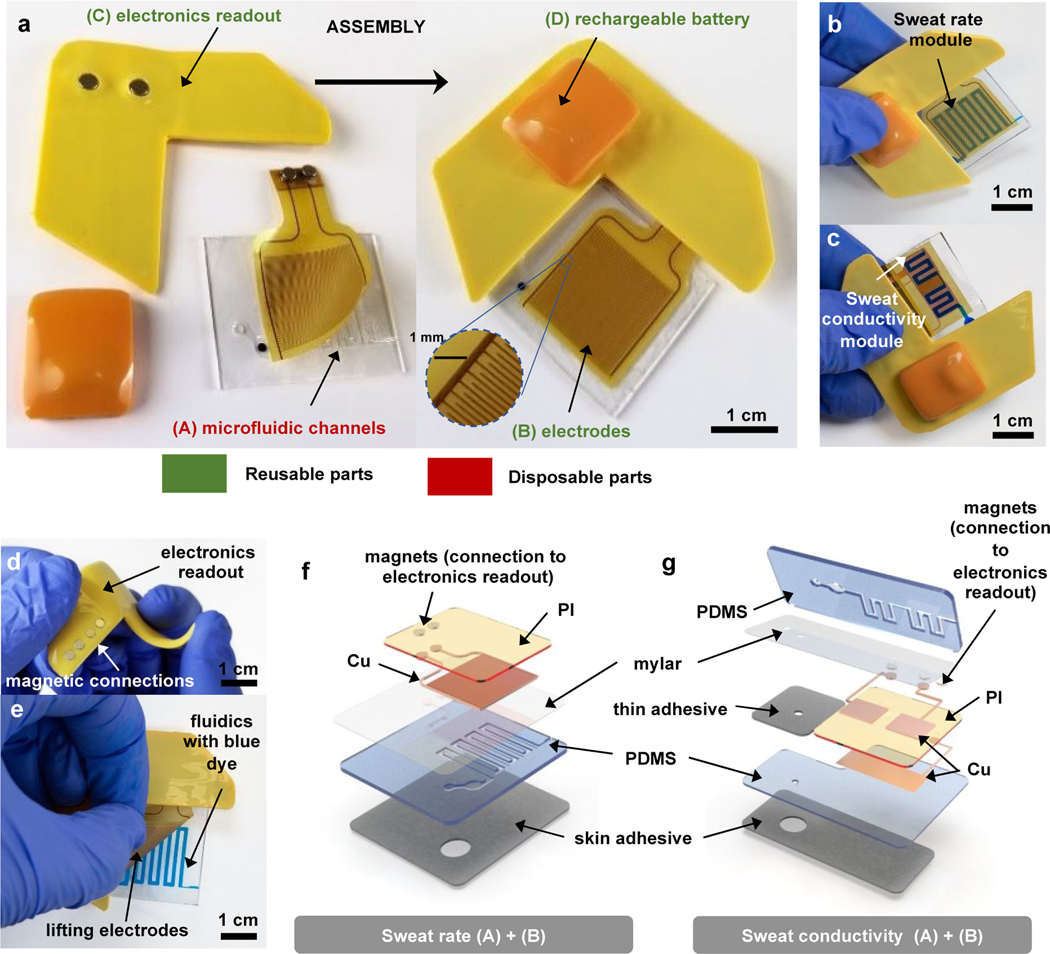
Figure 1. Pictures and schematic illustrations of a wireless microfluidics and electronics device with capabilities in digital measurements of sweat loss, sweat rate and sweat conductivity.
a. General overview of device assembly, showing disposable (A) and reusable (B, C, D) parts: microfluidics channels (A) are assembled to electrodes (B) through a thin silicone adhesive coating. Electrodes connection to electronics readout (C) ensured through magnets allows wirelessly transmission of data, using battery (D) as a powering source, connected through magnets to (C).
b. Fully assembled device for sweat rate measurements, with blue dyed liquid in the microfluidic channel to aid visualization.
c. Fully assembled device for sweat conductivity measurements, with blue dyed liquid in the microfluidic channel to aid visualization.
d. Bending of the electronics readout part, showing high flexibility and low profile.
e. Peeling of reusable electrodes from the microfluidics module, illustrating reusability of parts (B, C, D).
f. Exploded view schematic illustrations of parts (A) and (B) for the sweat rate device.
g. Exploded view schematic illustrations of parts (A) and (B) for the sweat conductivity device.