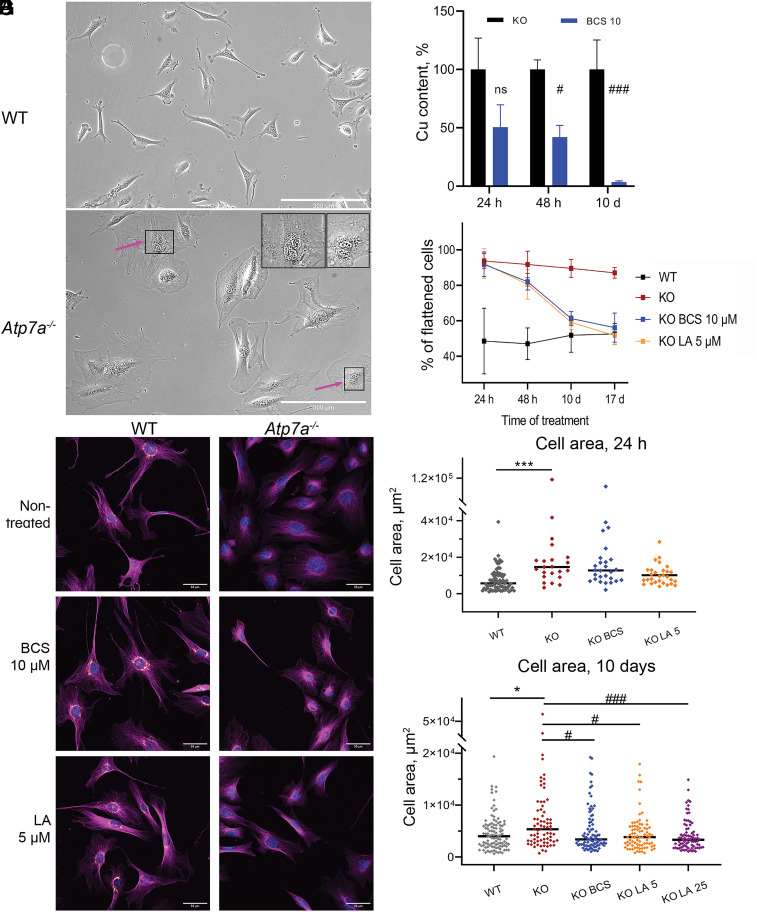
Fig. 1.
α-lipoic acid reverses Cu-dependent changes in cell morphology of Atp7a-deficient preadipocytes. (A) Fibrillar morphology of WT preadipocytes and (B) flattened phenotype of KO cells; changes in nuclei size are indicated with arrows in the zoomed upper-right corner of the panel (scale bar, 300 µm). (C) Cellular Cu content in KO preadipocytes is decreasing during treatment with 10 µM BCS. (D) The number of flattened KO cells is decreasing during treatment with 10 µM BCS (blue) and 5 µM LA (orange) compared to nontreated conditions (dark-red). (E) Morphological changes in KO preadipocytes after 17 d of treatment with 10 µM BCS or 5 µM LA compared to the WT cell line visualized with immunostaining. Magenta α-tubulin, orange Atp7a (scale bar, 50 µm). Changes in cell area after 24 h (F) and 17 d (G) of treatment with BCS or LA. Each dot corresponds to an individual cell. The black line represents the median cell area. Cell areas were determined using ImageJ software. For panels (C, F, and G): comparison to nontreated WT cells designated with asterisks (*); comparison with the nontreated KO cells designated with sharp (#); *, # P-value < 0.05; ***, ### P-value < 0.001.