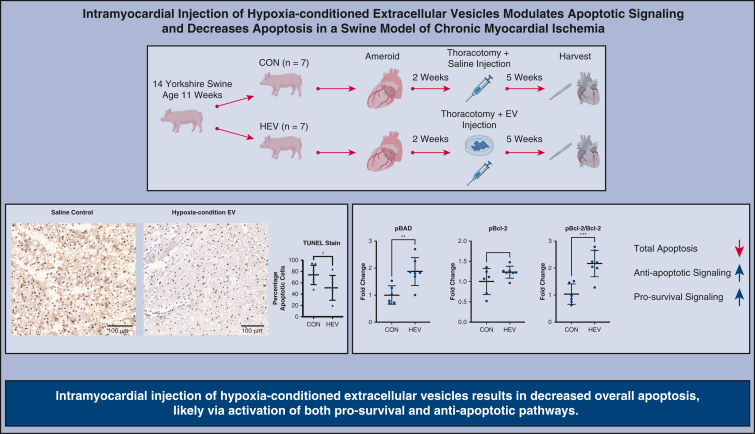
Figure 1.
Fourteen swine were assigned to 2 groups: saline control injection (CON) or hypoxia-conditioned extracellular vesicles (HEV). Swine underwent placement of an ameroid constrictor on the left coronary circumflex artery at age 11 weeks. Two weeks later, all swine underwent redo-left thoracotomy with injection of CON or HEV. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) stain showed a decrease in total apoptosis in the HEV group compared with control. Immunoblotting showed increased concentration of prosurvival and antiapoptotic proteins. Intramyocardial injection of hypoxia-conditioned extracellular vesicle results in decreased overall apoptosis, likely via activation of both prosurvival and antiapoptotic pathways. EV, Extracellular vesicles; pBAD, phospo-Bcl-2–associated death promoter-serine 112; pBcl-2, phospho-B-cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001.