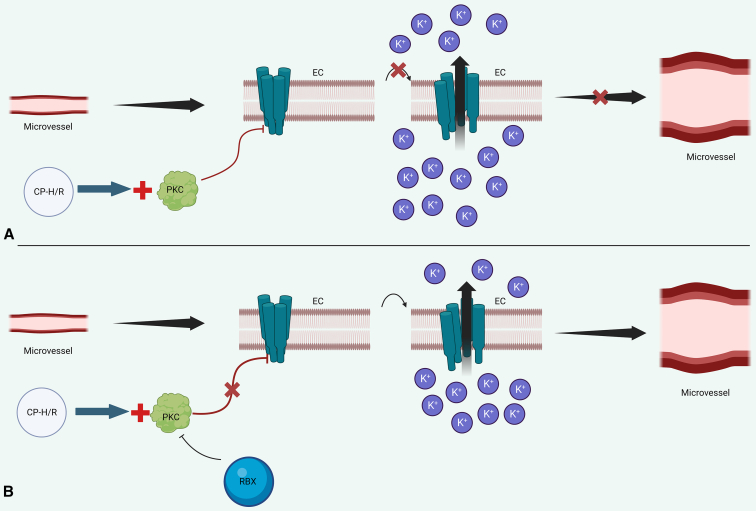
Figure 6.
Schematic of SK-channel–mediated vasodilation. A, CP-H/R increases PKC activity, which phosphorylates SK channels. This results in decreased SK-channel calcium sensitivity and reduces SK-channel opening, leading to reduced potassium currents and reduced endothelial hyperpolarization. This diminishes microvascular relaxation. B, RBX inhibits PKC, preventing PKC-mediated inhibition of SK-channel activity, thereby promoting endothelial hyperpolarization and coronary microvascular smooth muscle relaxation. SK channels are cyan on EC membranes. EC, Endothelial cell; CP-H/R, cardioplegic hypoxia–reoxygenation; PKC, protein kinase C; RBX, ruboxistaurin.