Figure 8.
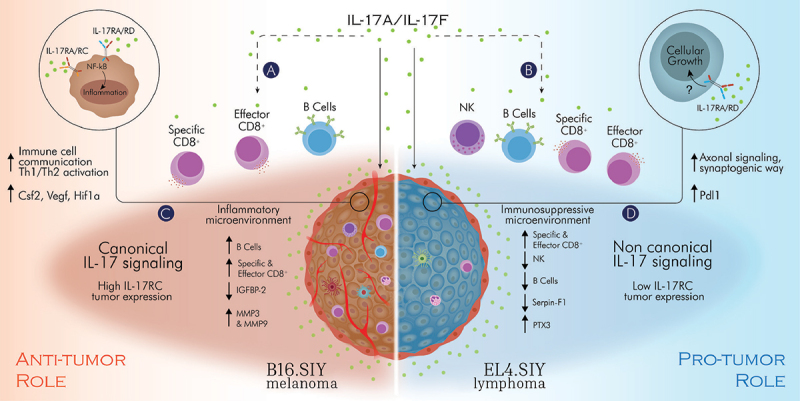
Proposed model of the role of the IL-17A/F:RA pathway in cancer.
The role of the IL-17A/F:RA pathway in cancer was investigated using syngeneic murine tumor models and IL-17 signaling deficient mice. Our results suggest contrasting effects of host IL-17 signaling on tumor growth, mediated by immune cell recruitment and specific anti-tumor cytotoxic CD8+ T responses (a,b), as well as IL-17 signaling in tumor cells (c,d) influencing tumor cell proliferation and the tumor microenvironment. Overall, IL-17 signaling in B16.SIY cells with high levels of IL-17RC activate a “canonical” pro-inflammatory IL-17 response, which, when combined with IL-17 induction of anti-tumor immunity, exerts a global anti-tumor role (c). Conversely, IL-17 signaling in EL4.SIY cells with low IL-17RC expression induces a “non-canonical” IL-17 response, promoting cell growth and inhibitory mediators of the immune response, ultimately leading to global pro-tumor effects (d). Model illustrated by @darwid_illustration.
