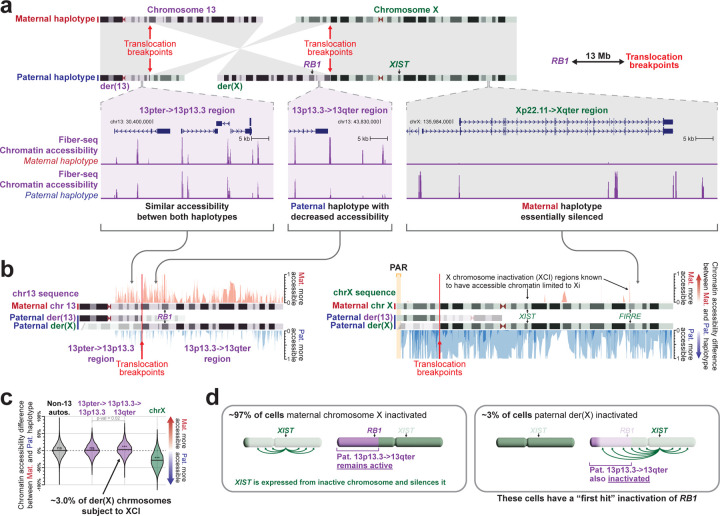
Figure 5 |. Inappropriate X chromosome inactivation of the RB1 locus along der(X).
a, (top) Idiogram showing the intact chromosomes 13 and X, as well as the derivative chromosomes 13 and X in the proband. Translocation breakpoints, and the location of the genes RB1 and XIST are highlighted. (bottom) Haplotype-resolved chromatin accessibility is displayed for loci across the der(13) and der(X) chromosomes. b, Difference in chromatin accessibility between the maternal and paternal haplotype across loci along chromosome 13 (left) and chromosome X (right). Regions with more red than blue signal have more chromatin accessibility along chr13int versus der(13) or chrXint versus der(X). c, Swarm plot showing the overall haplotype imbalance in chromatin accessibility along autosomes (except for chromosome 13), chromosome X, and two portions of chromosome 13. Specifically, the 13pter->13p13.3 region is present along chr13int and der(13), whereas the 13p13.3->13qter region is present along chr13int and der(X). P-value calculated using Mann-Whitney U-test. d, Model showing inappropriate XCI of the autosomal region along der(X) that contains the RB1 locus as the first hit for the development of bilateral retinoblastomas in this patient.