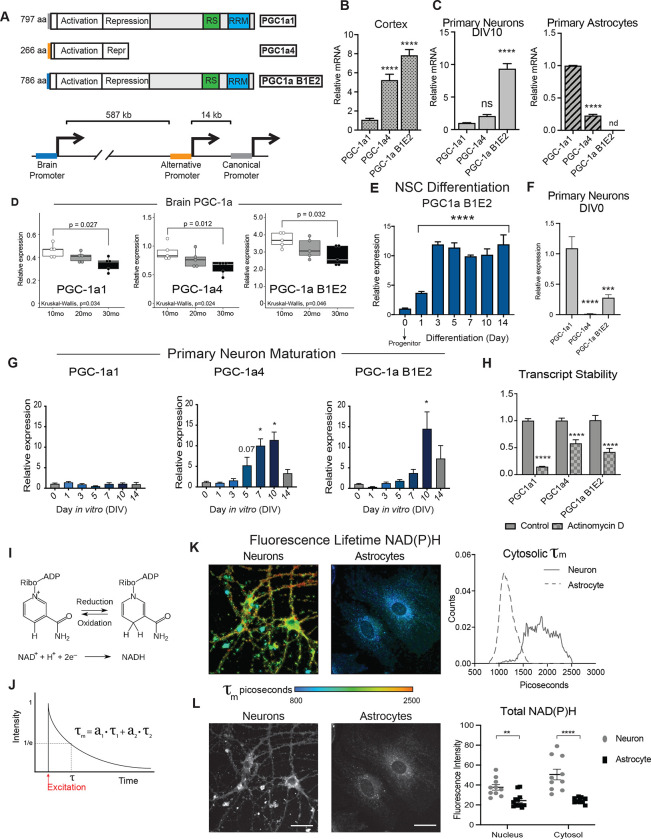
Figure 3: PGC-1a transcript isoforms in the brain and cell type specificity.
A) Schematic of the three major isoforms of Ppargc1a expressed in the brain and a representation of the location of their three distinct promoter regions. B-C) Relative expression pattern of PGC-1a transcripts detected by RT-qPCR of 12-month-old male mouse cortex (n=6) (B) and DIV10 primary cortical neurons and astrocytes isolated from P0 (neurons) and P1 (astrocytes) neonates (n=6) (C). D) RT-qPCR detection of Ppargc1a transcript variants in cortex of male mice at 10 months, 20 months, and 30 months old (n=5). E) Expression of the brain-specific isoform of PGC-1a during neural stem cell (NSC) differentiation (n=3). F) Relative expression pattern of PGC-1a transcripts detected in DIV0 P0 neurons by RT-qPCR (n=6).G) Detection of Ppargc1a transcript variants during maturation of P0 primary cortical neurons (n=3–6). H) PGC-1a transcript levels after 24 hours of actinomycin D treatment (n=7) I) Schematic of oxidation-reduction reaction of NAD+ to NADH. J) Example of two component decay curve produced through fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and is represented by the equation τm = a1(τ1) + a2(τ2). K) Representative images (left) and distributions (right) of NAD(P)H mean fluorescence lifetime images of primary neurons and primary astrocytes (n=10–12). L) Representative images (left) and quantitation (right) of NAD(P)H fluorescence intensity of primary neurons and primary astrocytes (n=10–12). Statistical significance determined by ANOVA (B, C, D, E, F, and G) and student’s t-test (I). Asterisks indicate p value of <0.05 (*), <0.01(**), <0.0001 (****).