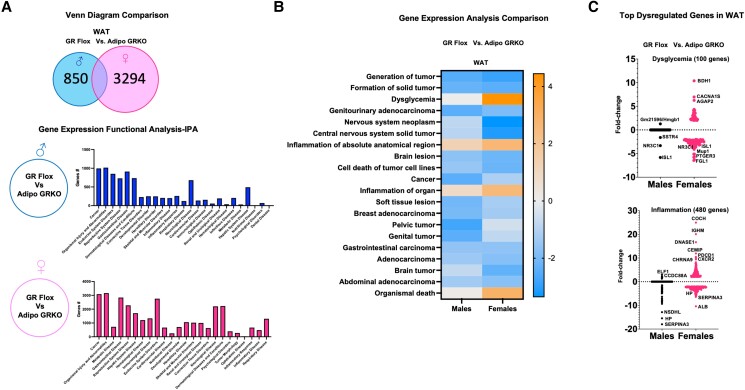
Figure 3.
Deletion of adipocyte GR significantly alters visceral white adipose tissue gene expression. (A) Venn diagram comparison between mesenteric adipose tissue of GR Flox and Adipo GRKO mice representing the number of differentially expressed genes in males and females. Functional clustering using the bioinformatics tool Ingenuity Pathway Analysis revealed several differentially regulated genes implicated in cancer, metabolic, and inflammatory diseases in both males and females. (B) Heat map generated from the microarray data comparing the gene expression analyzed from GR Flox and Adipo GRKO mice between males and females. Upregulated and downregulated genes associated with several pathologies, including cancer, dysglycemia, and inflammation, were associated with adipocyte GR deletion. (C) Pathologies linked to metabolic dysfunction such as dysglycemia and inflammation were among the top upregulated genes. Microarray analysis revealed enrichment of multiple dysglycemia and inflammation associated genes with a greater than 2-fold change in male and female Adipo GRKO mice.
Abbreviations: Adipo GRKO, adipocyte-specific GR knockout; GR, glucocorticoid receptors; GR Flox, C57BL/6J GR flox/flox.