Figure 7. Acod1 extinction boosts adaptive immunity and enhances immunotherapy.
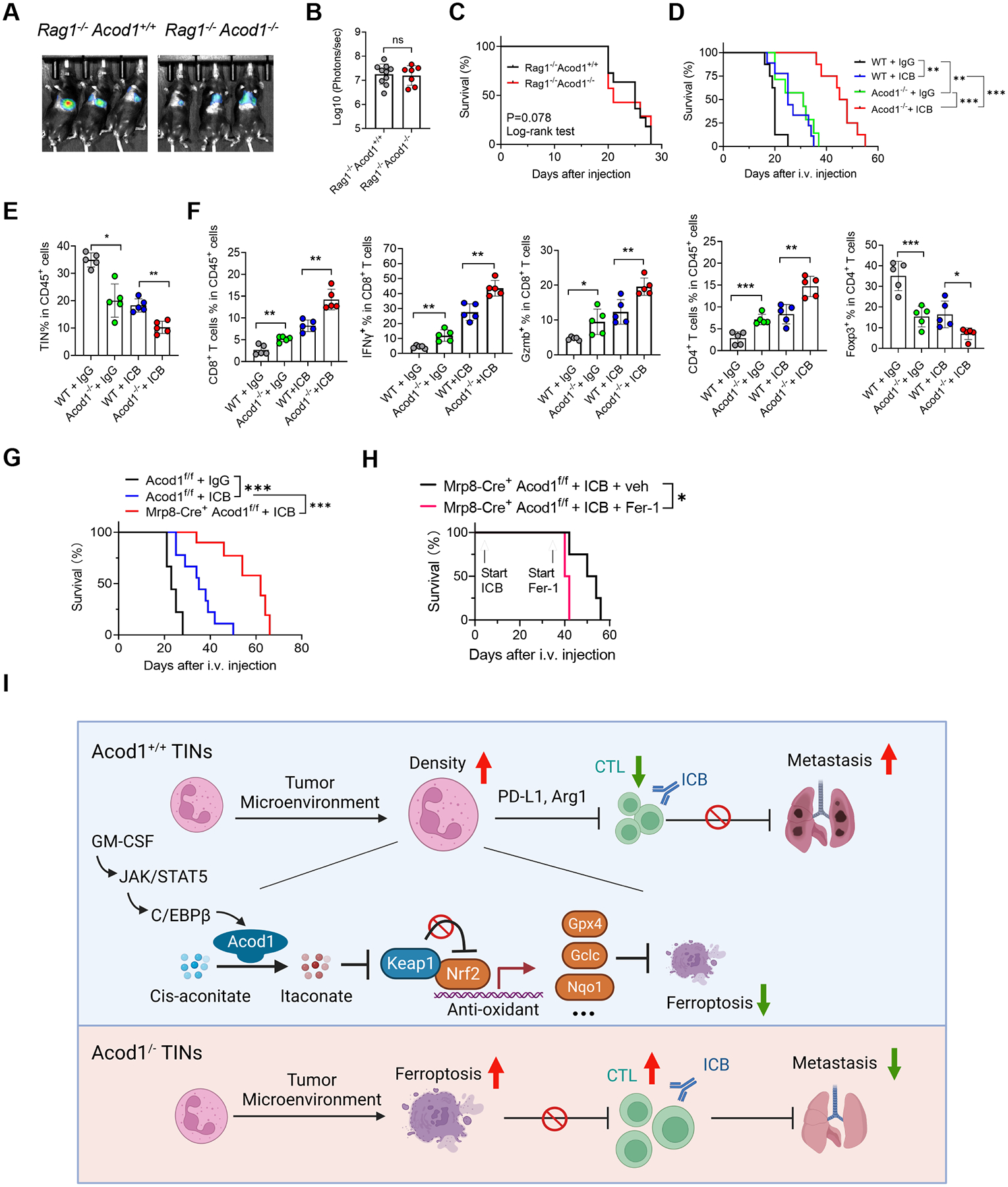
(A-C) Lung metastasis of E0771-TR in Rag1‒/‒Acod+/+ (n=11) and Rag1‒/‒Acod1‒/‒ (n=7) mice, established with the method illustrated in Figure 3A. Shown are representative BLI images (A), BLI quantification (B) and animal survival (C). (D) Survival of WT and Acod1‒/‒ mice (n=8–10) bearing E0771-TR lung metastasis and treated with isotype IgG or ICB (αPDL1 + αCTLA4, 10mg kg‒1 each, i.p., twice/week). (E-F) Flow cytometry to measure frequencies of TINs and T cell subsets from lungs of WT and Acod1‒/‒ interim cohorts 15 days after i.v. injection of E0771-TR (n=5 for each group). (G) Survival of Acod1f/f and Mrp8-cre+Acod1f/f mice bearing E0771-TR lung metastasis and treated with isotype IgG or ICB (αPDL1 + αCTLA4, 10mg kg‒1 each, i.p., twice/week, started three days after i.v. injection). n=10 for each group. (H) Survival of Mrp-8cre+Acod1f/f mice undergoing ICB treatment further treated with or without Fer-1 (2mg kg-1, i.p., once/2 days). Start timepoints of ICB and Fer-1 treatments were indicated, n=4 for each group. (I) Schematic of the mechanism and function of Acod1 in TINs to promote BC lung metastasis (created with BioRender). In B, E and F, data represent mean ± s.e.m.; ns, not significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, Mann-Whitney test (for B) or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (for E and F). In C, D, G and H, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, log-rank test. See also Figure S7.
