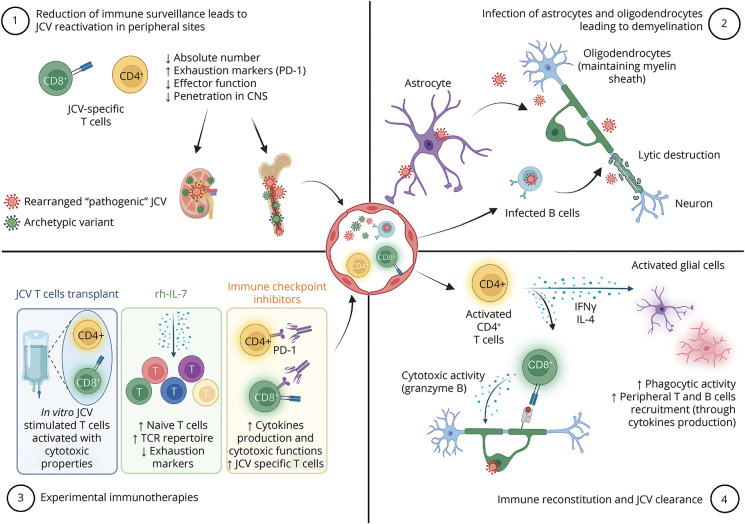
Figure. Radiologic and Pathologic Features in PML.
Representative MRI images showing canonical PML presentation with T2 hyperintense (A) and T1 hypointense (B) lesion of the frontal subcortical white matter and partially involving U fibers. In diffusion-weighted images, the lesion presents a demyelination front (C). Hematoxylin and eosin (HE, D, the position of the inset on the bottom and gray matter/white matter limit are highlighted by dashed lines), Luxol fast blue periodic acid–Schiff (LUPAS, E), and antineurofilament immunostained (NF, F) histologic sections show extensive white matter demyelination with relative preservation of axons. Numerous reactive astrogliosis (GFAP, G) and foamy macrophages (CD68, H) are found within the lesion. JC virus inclusions in nuclei of oligodendrocytes (double arrow in D) and astrocytes (simple arrows in D, G) are highlighted by SV40 immunostaining (I, simple arrows). T-cell infiltration is seen in the perivascular and interstitial spaces (CD3, J), accompanied by perivascular B cells (CD20, K). Scale bars = 5 mm (D–F) and 50 μm (inset on the bottom in D, G–K). PML = progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.