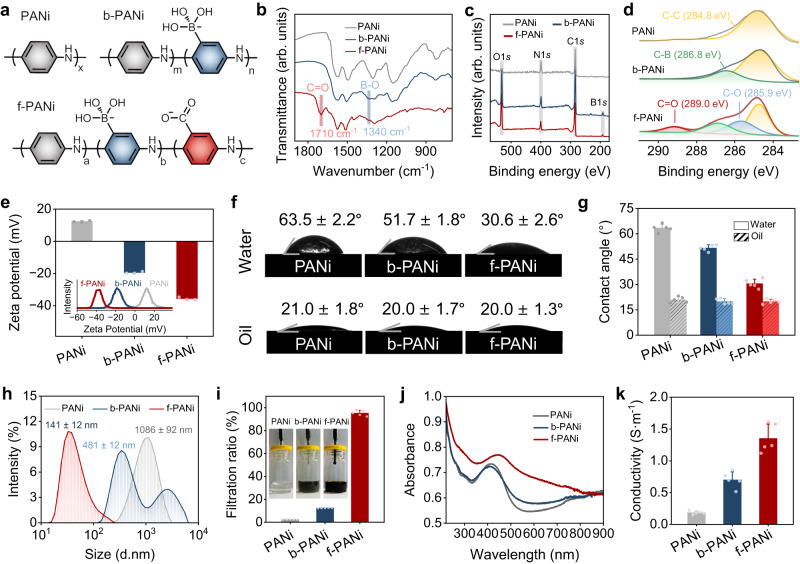
Fig. 2. Structure and properties of f-PANi.
a Chemical structures of the conducting polymers, including PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi. b FTIR spectra of PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi. c XPS survey for PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi. d High-resolution spectra of C1s for different conducting polymers. e Zeta potential of conducting polymer aqueous dispersions (n = 3 independent experiments). f Diagram of water and oil droplets wetting conducting polymer films. g Water and oil contact angles of PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi (n = 5 independent experiments). h The particle size of different conducting polymers dispersed in water. i Filtration ratio of PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi. Inset: Photographs of conducting polymer aqueous dispersions passed through a membrane filter (n = 5 independent experiments). j UV–vis absorbance spectra of PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi aqueous dispersions. k Conductivity of PANi, b-PANi, and f-PANi (n = 5 independent experiments). PANi: polyaniline, b-PANi: borated polyaniline, f-PANi: functionalized polyaniline. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation in (e, g, i, k).