Figure 9.
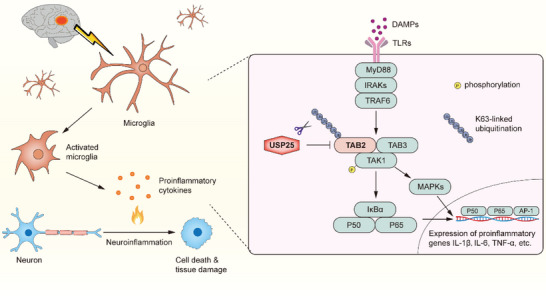
Schematic illustration of the role of USP25 in ischemic stroke injury. After ischemic stroke, microglia are activated and produce proinflammatory cytokines, which promote neuronal death and tissue damage. In this process, USP25 inhibits the activation of NF‐κB and MAPK signaling pathways in microglia by removing K63‐specific polyubiquitin chains from TAB2, thereby ameliorating neuroinflammation and cerebral injury.
