Figure 2.
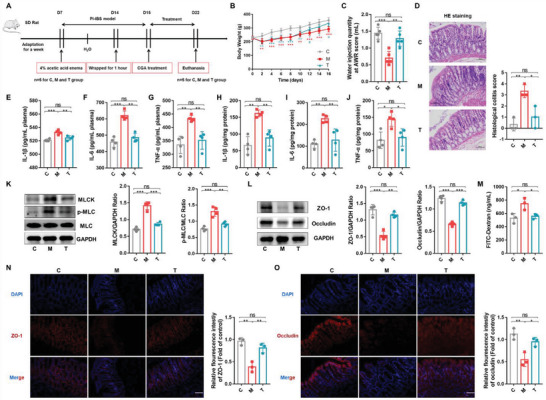
Rectal administration of CGA alleviated AA‑induced PI‐IBS in rats. A) Experimental scheme of rectal administration of CGA in PI‐IBS rats (n = 5). B) Changes in body weight following CGA treatment (n = 5). C) Water injection rate when the AWR score was 3 (n = 5). D) H&E staining and pathological score of colon sections (n = 3). E–J) Concentrations of the representative proinflammatory cytokines IL‐1β, IL‐6 and TNF‐α in rat serum and colon tissue (n = 4). K) Expression of key proteins of the MLCK/p‐MLC signaling pathway in rat colon tissue samples (n = 4). L) The expression of TJ proteins (ZO‐1, Occludin) in rat colon tissue (n = 4). M) Measurement of gut permeability in rats (n = 3). N,O) Immunofluorescence staining of TJ protein (ZO‐1, Occludin) expression in the colonic section (n = 3). C, control group; M, PI‐IBS rat group; T, PI‐IBS rats rectally administered CGA group. Scale bar, 100 µm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. ns, p > 0.05; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. CGA: chlorogenic acid.
