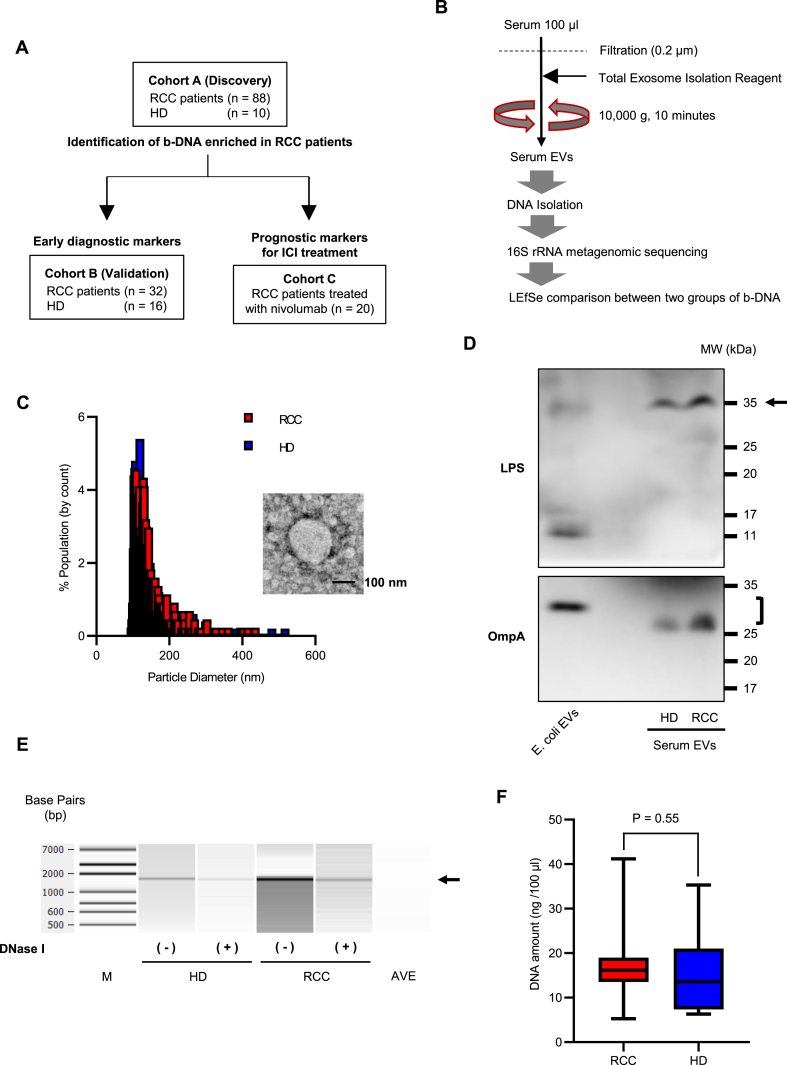
Fig. 1.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) collection from serum and isolation of bacteria-derived DNA (b-DNA) (A) Study flow diagram. (B) Methods of processing and analyzing serum samples. (C) Representative results of nanoparticle and transmission electron microscopic analysis of EVs isolated from serum samples. A black bar indicates 100 nm. (D) Western blot analysis of serum EVs from a patient with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and a healthy donor (HD) using an anti-E.coli LPS or an anti-OmpA antibody. (E) DNase I treatment of serum EVs followed by 16S rRNA gene amplification by PCR. Amplified PCR products are analyzed using Bioanalyzer. M: DNA ladder, AVE: buffer AVE. (F) DNA amount in EVs in serum 100 μL from 88 patients with RCC and 10 HD. Comparison between the two groups is performed by the Mann–Whitney U test.