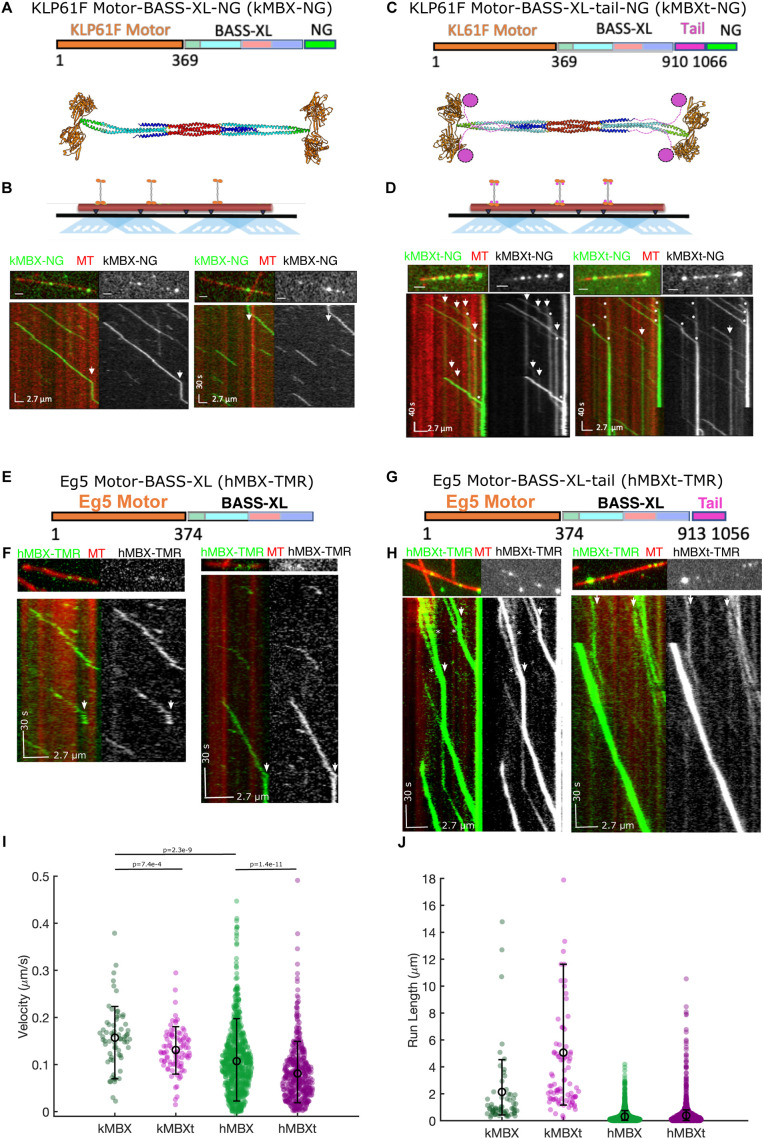
FIGURE 2:
Kinesin-5 minitetramers undergo processive motility interrupted by static pauses along MTs in vitro. A) Top, kMBX domain organization. Motor- and neck-linker domains (1–365, blue) extended coiled-coil (green), BASS-XL minifilament with its dimerized zone (orange), tetrameric zone (red), and C-terminal zone (cyan). Middle, structural model for the kMBX minitetramer as shown in Figure 1D. B) Top, TIRF microscopy reconstitution setup to examine kMBX motors motility along MTs. Middle panel, image of individual MTs (red) with kMBX motors (green). Bottom panel, kymographs of the above image with kMBX motor motility along MTs revealing their processive motility with extended pauses (arrows) and do not accumulate at MT plus-ends. C) Top, kMBX domain organization. Motor- and neck-linker domains (1–365, orange) extended coiled-coil (green), BASS-XL minifilament with its dimerized zone (cyan), tetrameric zone(red), C-terminal zone (blue) and C-terminal tail domain (pink). Middle, structural model for the kMBX minitetramer as shown in Figure 1D. D) Top, TIRF microscopy setup for kMBXt MT-motility assays. Middle panel, images of individual MTs (red) with kMBXt motors (green). Bottom panel, kymograph of the above image with kMBXt motor motility along MTs. Motor assembly into clusters is marked by an asterisk, and motor pauses are marked by arrowheads. E) The hMBX minitetramer consists of the human Eg5 motor-neck linker domain (1–374, orange), the D. melanogaster BASS domain (597–799) with its extended coiled-coil (green), with its dimerized zone (cyan), tetrameric zone (red), C-terminal zone (blue). F) Top panel, image of individual MT (red) with hMBX motors (green). Bottom panel, kymographs of the above image with hMBX motor motility along MTs revealing their processive motility with short pauses (arrows) and do not accumulate at MT plus-ends. G) The hMBXt-TMR minitetramer consists of the human Eg5 motor–neck linker domain (1–374, orange), the D. melanogaster BASS-XL minifilament (597–799) with its extended coiled-coil (green), with its dimerized zone (cyan), tetrameric zone(red), C-terminal zone (blue) and the human Eg5 C-terminal tail domain (913–1056, pink). H) Top panel, images of individual MTs (red) with hMBXt-TMR motors (green). Bottom panel, kymographs of the above image with hMBXt motor motility along MTs. Motor assembly into clusters is marked by an asterisk, and motor pauses are marked by arrowheads. I) Histogram distributions for velocity (μm/s) of the kMBX (green), kMBXt (pink), hMBX (green), and hMBXt (pink) motors along MTs showing that the kMBXt or hMBXt undergo slower motility than the kMBX and hMBX motors. T tests show highly significant differences between kMBX and kMBXt as well as hMBX and hMBXt. There are no significant differences between hMBXt and kMBXt motor velocities. J) Histogram distributions for motility run lengths (μm) of the kMBX (green), kMBXt (pink), hMBX (green), and hMBXt (pink) motors along MTs revealing that the kMBXt or hMBXt motors are generally more processive than the hMBX and kMBX motors.