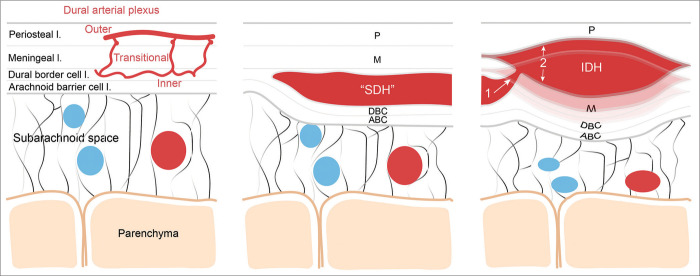
Figure 4:
Schematic representation of the putative pathophysiological mechanisms leading to the formation of the interdural hematoma. Left, schematic illustrating the normal meningeal layer microanatomy including the dural arterial plexus (layer thickness is not scaled). From external to internal meningeal layer: the periosteal layer (P), the meningeal layer (M), the dural border cell layer (DBC), and the arachnoid barrier cell layer (ABC); middle, illustration of the microanatomical localization of the classic subdural hematoma contained by the DBC; Right, the putative mechanism leading to the formation of the IDH through higher pressure blood dissecting more superficially the dural layers from the vascularized inner DBC layer. SDH: Subdural hematoma, IDH: Interdural hematoma.