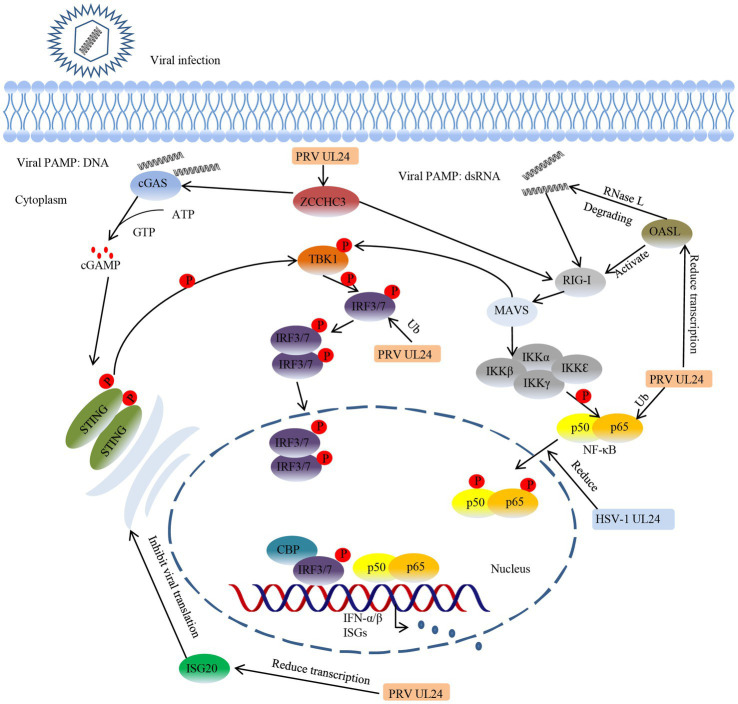
Figure 2.
HSV-1 UL24 and PRV UL24 evade innate immunity by inhibiting the cGAS/STING and RIG-I signaling pathways. The host innate immune system can recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), thereby initiating innate immune responses and subsequent adaptive immune responses. Viral PAMPs containing herpesvirus DNA and dsRNA, PRV UL24 and HSV-1 UL24 can inhibit the innate immunity induced by viral PAMPs. PRV UL24 downregulates the expression of the antiviral factors ISG20, OASL and ZCCHZ3 and promotes the degradation of IRF7 and p65 to inhibit the host immune response. HSV-1 UL24 can reduce the entry of NF-κB subunits p50 and p65 into the nucleus to block the signal transmission of the immune pathway.