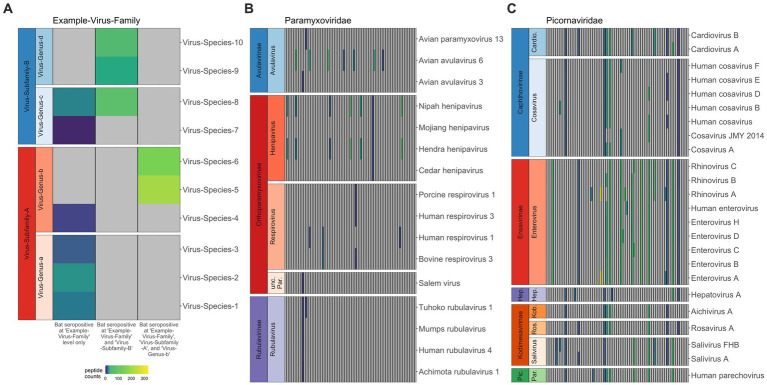
Figure 1.
Co-infection or broad binding of antibodies to closely-related antigens across the peptide library for Pteropus alecto. When antibodies in serum from a single individual bound antigens from multiple subfamilies in the same virus family, we interpreted this as a single exposure to one family; likewise, when antibodies bound antigens from multiple genera within the same subfamily, we interpreted this as a single exposure to that entire subfamily; and when antibodies bound antigens from multiple virus species in the same genus, we interpreted this as a single exposure to that genus (A). Viral species (y-axis) are sorted according to viral subfamily and genus, thus the related viruses (e.g., within the same clade) are clustered together. Each column represents data for a distinct individual, and gray panels indicate 0 peptide hits; colors represent positive hit values, following legend. The human-focused PhIP-Seq library effectively distinguishes infections in bats, though it does better within bat-specific clades (B) than within human-specific clades (C), where we see a lot of antibody cross reactivity across genera.