Figure 2. Primary and Secondary End Points over the Course of the Trial.
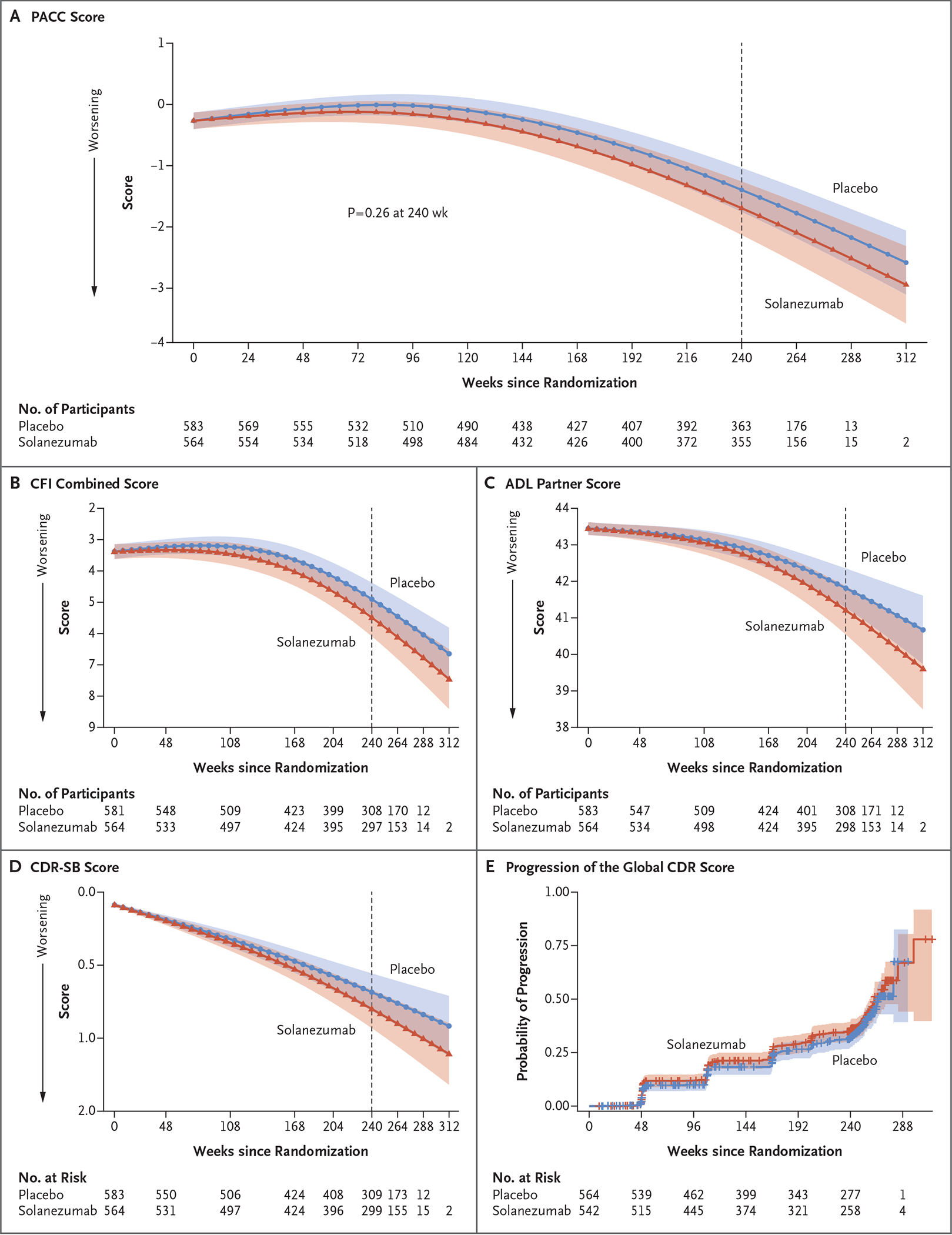
All panels show results for the modified intention-to-treat population. The 95% confidence intervals (indicated by shaded regions) were adjusted for multiplicity according to the prespecified graphical testing scheme. Panel A shows the primary end point, the Preclinical Alzheimer Cognitive Composite (PACC) score. The PACC is the sum of four z scores, with higher scores indicating better cognitive performance. The adjusted means, 95% confidence intervals, and P value were estimated with the use of a natural cubic spline model. Panel B shows the spline model–adjusted mean Cognitive Function Index (CFI) combined score (participant and partner). Scores for participant or partner range from 0 to 15, with higher scores indicating greater subjective concerns about cognitive function (range for combined score, 0 to 30). Panel C shows the spline model–adjusted mean score on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Prevention Questionnaire, as assessed by the participant’s partner. Scores range from 0 to 45, with higher scores indicating more difficulty in performing activities of daily living. Panel D shows the spline model–adjusted mean Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR)–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB) score. Scores range from 0 to 18, with higher scores indicating greater impairment in global functioning. Panel E shows Kaplan–Meier estimates of progression of the global CDR score, defined as two consecutive scores greater than zero or a final-visit score greater than zero. Global CDR scores range from 0 to 3, with 0 indicating no cognitive impairment and 3 indicating severe dementia.
