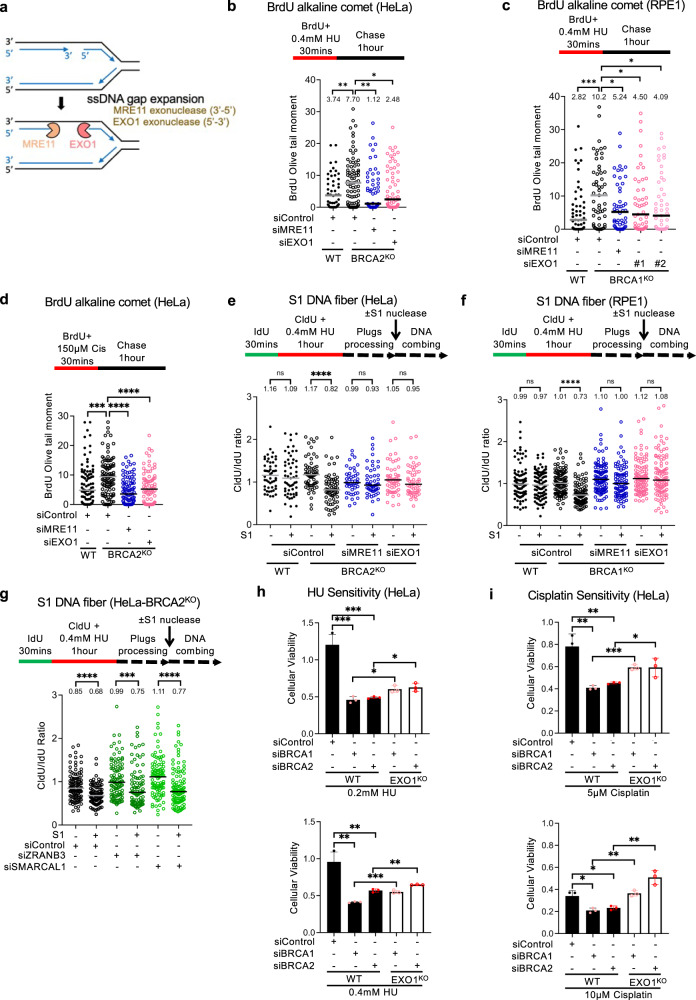
Fig. 1. Loss of EXO1 suppresses the accumulation of nascent strand ssDNA gaps induced by replication stress in BRCA-deficient cells.
a Schematic representation of the ssDNA gap expansion model tested: MRE11 extends the gap from the 3’ end and EXO1 extends it from the 5’ end. b, c BrdU alkaline comet assay showing that EXO1 knockdown suppresses the accumulation of replication-associated ssDNA gaps induced by treatment with 0.4 mM HU in HeLa-BRCA2KO (b) and RPE1-BRCA1KO (c) cells, similar to MRE11 depletion. At least 50 nuclei were quantified for each condition. The median values are marked on the graph and listed at the top. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (Mann–Whitney, two-tailed). A schematic representation of the assay conditions is shown at the top. Western blots confirming the EXO1 and MRE11 knockdown are shown in Supplementary Fig. S1a, b. d BrdU alkaline comet assay showing that EXO1 knockdown suppresses the accumulation of replication-associated ssDNA gaps induced by treatment with 150 µM cisplatin in HeLa-BRCA2KO cells, similar to MRE11 depletion. At least 75 nuclei were quantified for each condition. The median values are marked on the graph and listed at the top. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (Mann–Whitney, two-tailed). A schematic representation of the assay conditions is shown at the top. e, f S1 nuclease DNA fiber combing assays showing that knockdown of EXO1 suppresses the accumulation of nascent strand ssDNA gaps induced by treatment with 0.4 mM HU in HeLa-BRCA2KO (e) and RPE1-BRCA1KO (f) cells, similar to MRE11 depletion. The ratio of CldU to IdU tract lengths is presented, with the median values marked on the graphs and listed at the top. At least 45 tracts were quantified for each sample. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (Mann–Whitney, two-tailed). Schematic representations of the assay conditions are shown at the top. g S1 nuclease DNA fiber combing assays showing that knockdown of ZRANB3 or of SMARCAL1 does not affect the accumulation of nascent strand ssDNA gaps induced by treatment with 0.4 mM HU in HeLa-BRCA2KO cells. The ratio of CldU to IdU tract lengths is presented, with the median values marked on the graphs and listed at the top. At least 90 tracts were quantified for each sample. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (Mann–Whitney, two-tailed). Schematic representations of the assay conditions are shown at the top. Western blots confirming the ZRANB3 and SMARCAL1 knockdown are shown in Supplementary Fig. S1c,d. h, i Cellular viability assays showing that loss of EXO1 partially suppresses the HU (h) and cisplatin (i) sensitivity of BRCA1- or BRCA2-knockdown HeLa cells, at two different concentrations as indicated. The average of three independent experiments, with standard deviations indicated as error bars, is shown. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (t test, two-tailed, unpaired). Western blots showing EXO1 deletion are shown in Supplementary Fig. S3b. Source data are provided as a Source data file.