Figure 3.
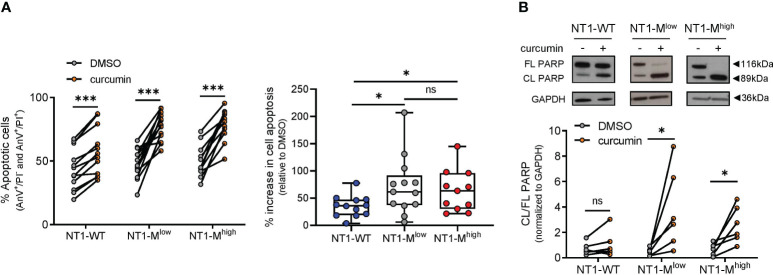
NT1-M CLL cells are more susceptible than NT1-WT to curcumin-induced apoptosis. Primary CLL NT1-WT (N = 12); NT1-M with a mutation allelic burden ranging from 0.03% to 12%, referred to as NT1-Mlow (N = 13); and NT1-M with a mutation allelic burden higher than 12%, referred to as NT1-Mhigh (N = 11), were incubated with curcumin (15 µM) or DMSO (0.05%) for 24 h. (A) Apoptosis was assessed by annexin V/PI (AnV/PI) assay, which allows distinguishing viable (AnV−/PI−), early apoptotic (AnV+/PI−), late apoptotic (AnV+/PI+), and necrotic cells (AnV−/PI+). Dot-and-line diagram (left) of apoptotic (early plus late) cells. ***P< 0.001, according to Wilcoxon paired test. Box and whisker with data points (right) of the percentage increase in the apoptosis of curcumin-treated NT1-WT, NT1-Mlow, and NT1-Mhigh CLL cells, normalized to their respective DMSO controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P< 0.05; ns, not significant, according to Mann–Whitney unpaired test. (B) Representative Western blot (top) showing full length (FL) and cleaved (CL) PARP and dot-and-line diagram of CL/FL PARP ratio (bottom) in NT1-WT, NT1-Mlow, and NT1-Mhigh CLL cells (N = 6, per group), incubated with curcumin or DMSO. *P< 0.05; ns, not significant, according to Wilcoxon paired test.