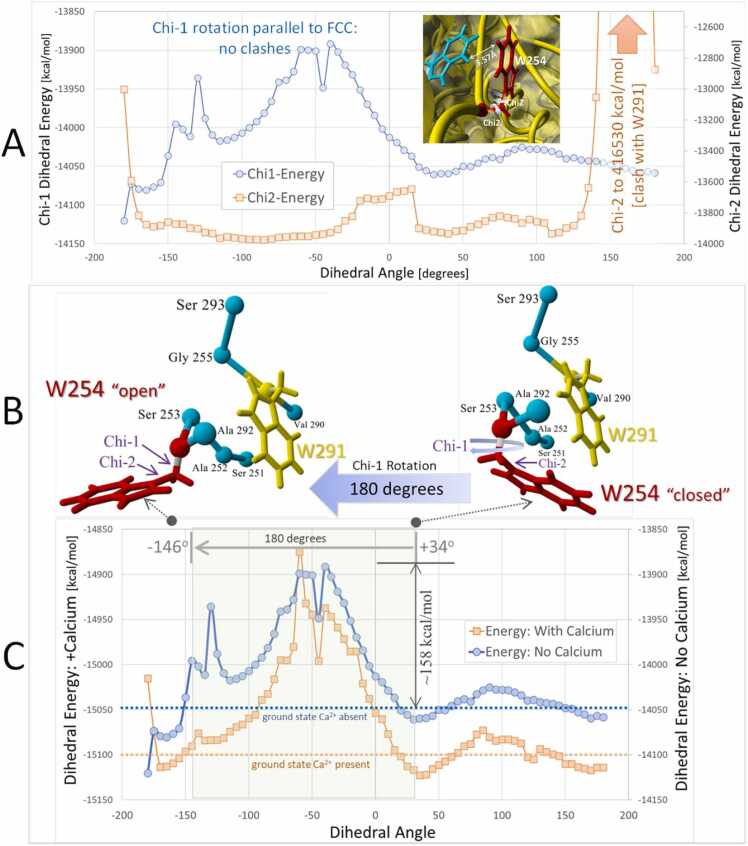
Fig. 3.
[A]: Comparison of chi-1 (N,CA,CB,CG; blue line) and chi-2 (CA,CB.CG,CD1; orange line) dihedral barrier scans for W254 in PDB 5JXG. The 360-degree scans were produced over 80 steps at 4.5-degrees per step (see Methods). Rotation about the W254 chi-2 dihedral bond resulted in an insurmountable clash with W291 located about 3.57 Å from W254. The energy barrier for this clash exceeded 416,000 kcal/mol). No serious sidechain clashes were observed for chi-1 rotation. [B] Details of W254 rotation about its chi-1 torsion bond. Rotation of this bond in the intMD docking simulations using 5JXG was from right to left (large blue arrow) starting at + 34 degrees (W254 in “closed” orientation) through 180-degrees and terminating at approximately − 145 degrees (W254 in “open” orientation). [C] Comparison of W254 chi-1 dihedral barrier scans for 5JXG with (orange line) and without (blue line) the four chelated calcium ions. The chi-1 peak energy barrier was approximately 158 kcal/mol for the Ca-free receptor and 230 kcal/mol for the receptor with Ca. The presence of Ca ions resulted in an overall (global) reduction in the chi-1 energy landscape by about 50–60 kcal/mol.