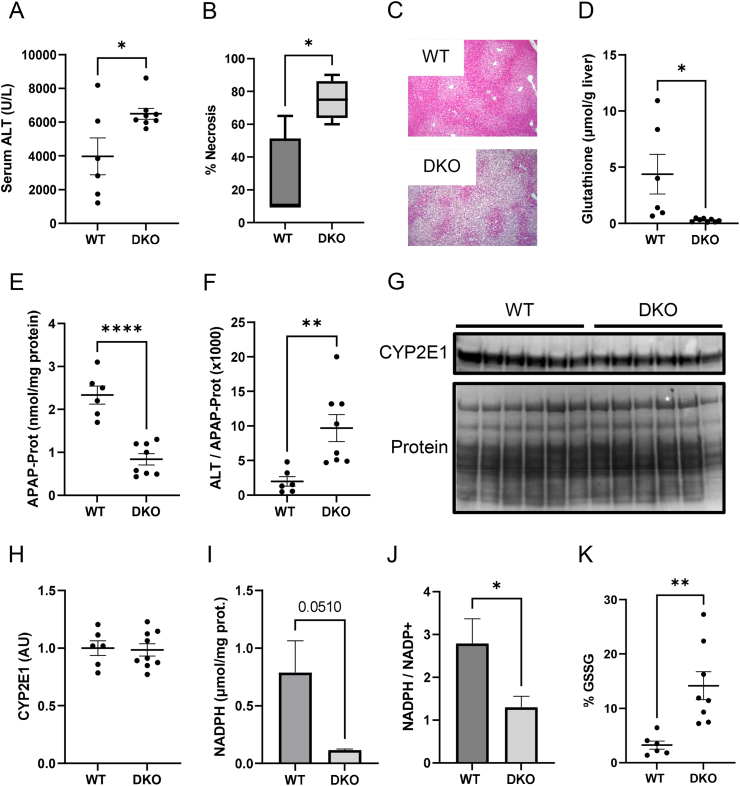
Figure 3.
MPC2/ALT2 double-knockout signficantly worsens liver injury and prevents glutathione recovery after APAP overdose. Male liver-specific MPC2/ALT2 DKO mice 10–16 weeks old were treated with 300 mg/kg APAP. Serum and liver tissue were collected 6 h later. (A) Serum ALT activity was measured in the WT and DKO mice. (B) Necrosis was quantified from H&E-stained liver sections. (C) Representative liver sections from WT and DKO mice at 100× magnification. (D) Total glutathione (GSH + GSSG) was measured in liver tissues. (E) APAP-protein adducts (APAP-Prot) were measured in liver tissue homogenates. (F) ALT was normalized to APAP-Prot. (G) CYP2E1 levels were measured in liver homogenates by immunoblot. Total protein on the immunoblot membrane was stained using Coomassie blue. (H) Densiometric analysis was performed on the CYP2E1 immunoblot in (G). (I) NADPH was measured in liver tissue homogenates. (J) NADP+ was also measured in liver tissue and NADPH was normalized to NADP+ to determine their ratio. (K) Oxidized glutathione (GSSG) was measured and expressed as the proportion of total glutathione. Comparison of two means was performed by two-tailed t-test. Comparison of three or more groups was performed by ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey's test for multiple comparisons. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. In all panels, lines and error bars indicate mean ± SE. Circles show individual data points and sample sizes. Box plots show medians and IQR.