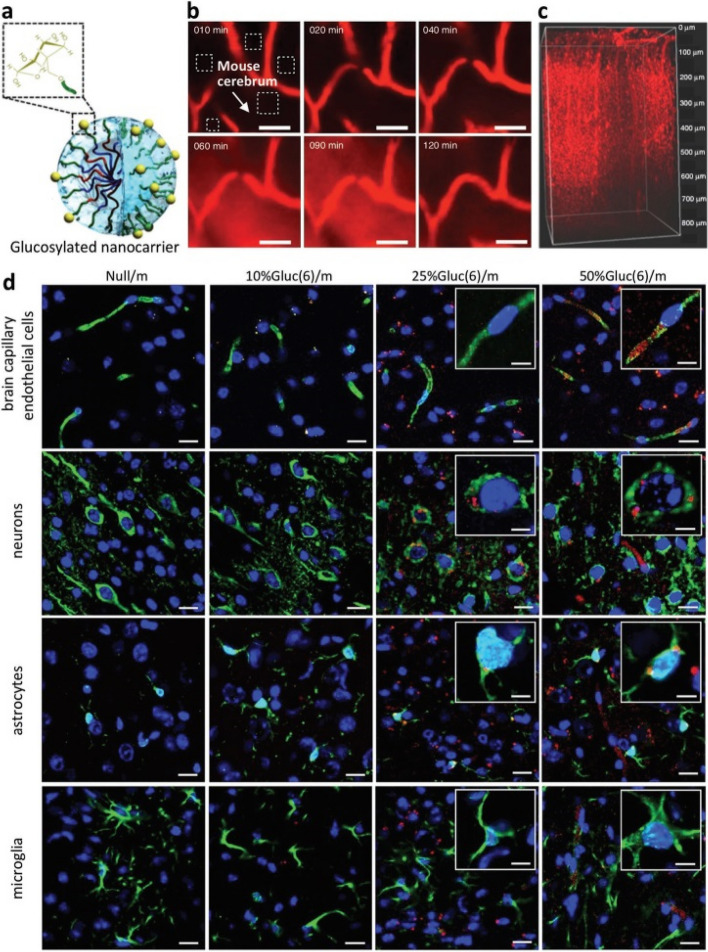
Fig. 24.
The use of nanocarriers to target the blood–brain barrier (BBB). The nanocarriers are modified with a glucose ligand on their surface (referred to as Gluc(6)/m), which allows them to bind to receptors in the BBB. Real-time observations show that the 25%Gluc(6)/m nanocarriers can successfully cross the BBB. Intravital multiphoton microscopy images of mouse cerebrum 48 h after administration show the presence of Gluc(6)/m nanocarriers (in red) in the brain. Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brains after administration of Null/m, 10%Gluc(6)/m, 25%Gluc(6)/m, and 50%Gluc(6)/m (in red) for 48 h, while the brain capillary endothelial cells, neurons, microglia, and astrocytes are stained in green color. These results demonstrate the potential of the Gluc(6)/m nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery to the brain. Reprint from [34] with a permission from Wiley