Figure 6.
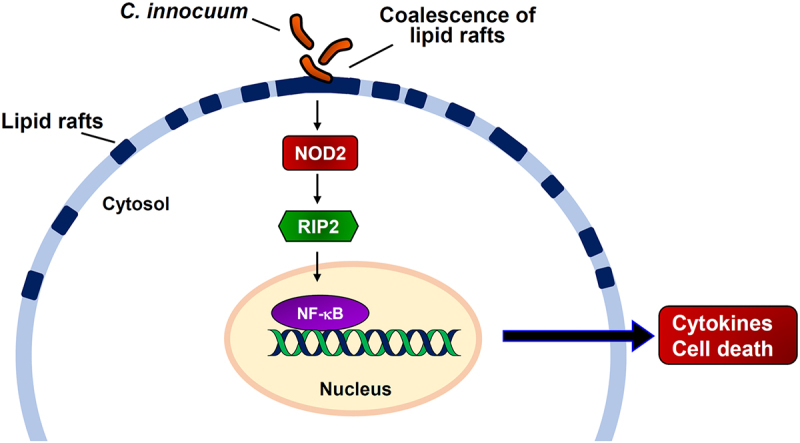
Hypothesized model illustrates C. innocuum-induced pathogenicity of intestinal epithelial cells. C. innocuum infection coalesces lipid rafts on the cell membrane, which then activates NOD2 pathway to promote NF-κB translocation in the nucleus, resulting in exacerbates cytotoxicity and inflammation of intestinal epithelial cells.
