Fig. 5.
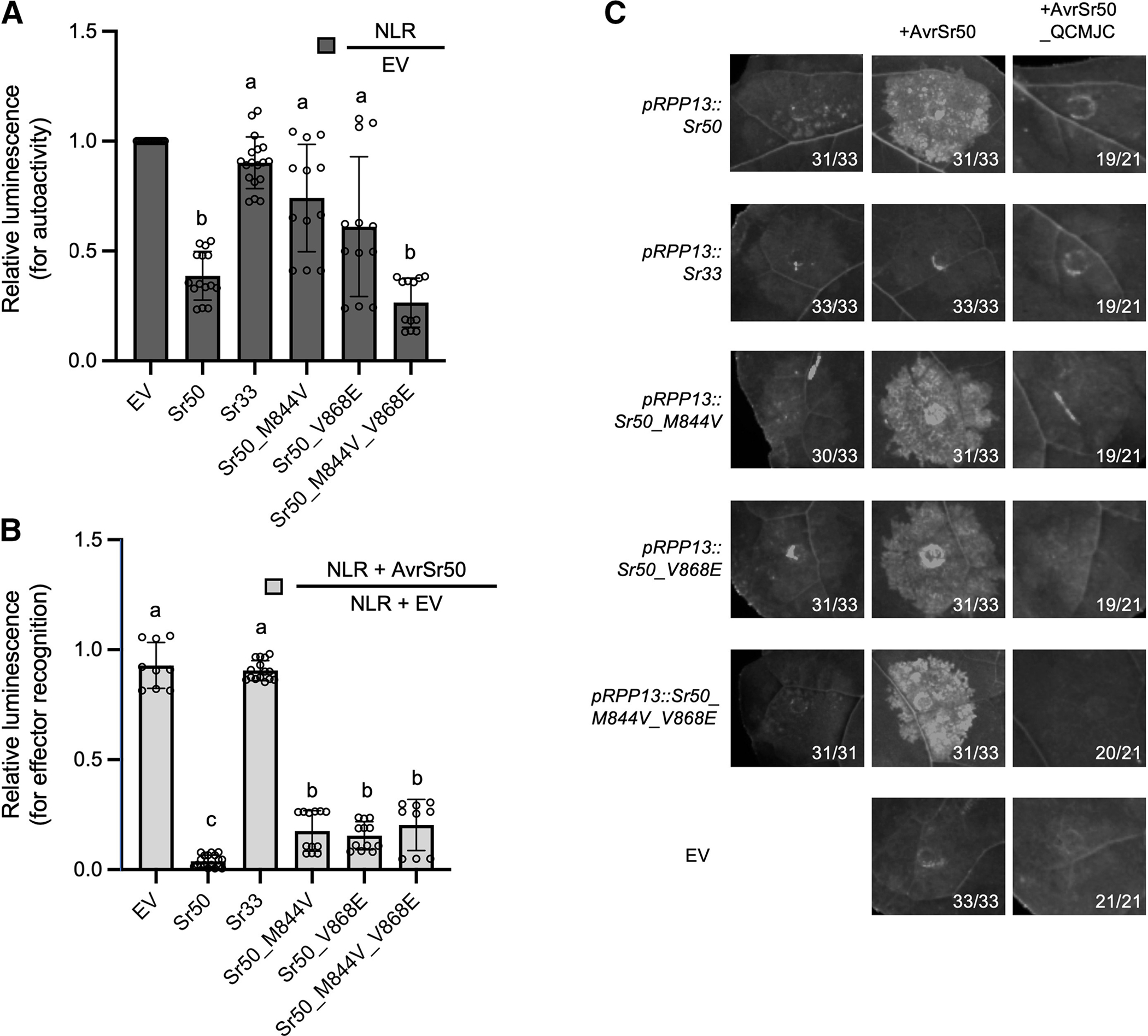
Sr50 autoactivity is decreased through mutations in its leucine-rich repeats (LRRs). A, Single mutants of Sr50 show decreased autoactivity in wheat protoplasts compared with wild-type Sr50, while the double mutant shows wild type–like autoactivity. We introduced single and double amino-acid changes into the nucleotide-binding LRR receptor (NLR) Sr50 to decrease its autoactivity. The sites were changed to the corresponding amino acids in that position within Sr33, as this NLR does not exhibit the same autoactivity phenotype in wheat protoplasts. Luciferase activity was determined approximately 36 h after transfection as a proxy for cell death. The relative luminescence reflects changes driven by autoactivity, and the low relative luminescence level indicates cell deaths by strong autoactivity. This value was obtained by normalizing the luminescence of each NLR construct by the luminescence obtained from the empty vector (EV) transfection. All values obtained in at least three independent experiments are indicated by dots and error bars indicate standard deviation. The equality of group means was assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and subsequent Tukey post-hoc tests. The samples assigned the same letter (a or b) do not show statistically significant differences (P ≥ 0.05), while those assigned different letters do (P < 0.05). B, Single mutants and double mutants of Sr50 induce cell death in response to AvrSr50. Luciferase activity was determined approximately 36 h after transfection as a proxy for cell death. The relative luminescence reflects the changes driven by effector recognition, and the low relative luminescence level represents cell deaths by effector recognition. This value was obtained by normalizing the luminescence of each NLR construct (or EV as a control) in the AvrSr50 co-transfection by the luminescence of that NLR construct in the EV co-transfection. All values obtained in at least three independent experiments are indicated by dots, and error bars indicate standard deviation. The equality of group means was assessed by one-way ANOVA and subsequent Tukey post-hoc tests. The samples assigned the same letter (a, b, or c) do not show statistically significant differences (P ≥ 0.05), while those assigned different letters do (P < 0.05). C, Single and double mutants of Sr50 induce cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana in response to AvrSr50. None of the NLRs initiated cell death in response to the effector variant AvrSr50_QCMJC. Leaves of 4- to 5-week-old N. benthamiana plants were infiltrated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying NLRs and effectors at an optical density at 600 nm = 0.3 and 0.4, respectively. UV images were taken on a BioRad Gel Imager 3 to 5 days after infiltration. Numbers on images correspond to the numbers of leaves that showed the depicted phenotype. Expression of NLRs was driven by the pRPP13 promoter, whereas effectors were driven by p35S.
