Fig. 7.
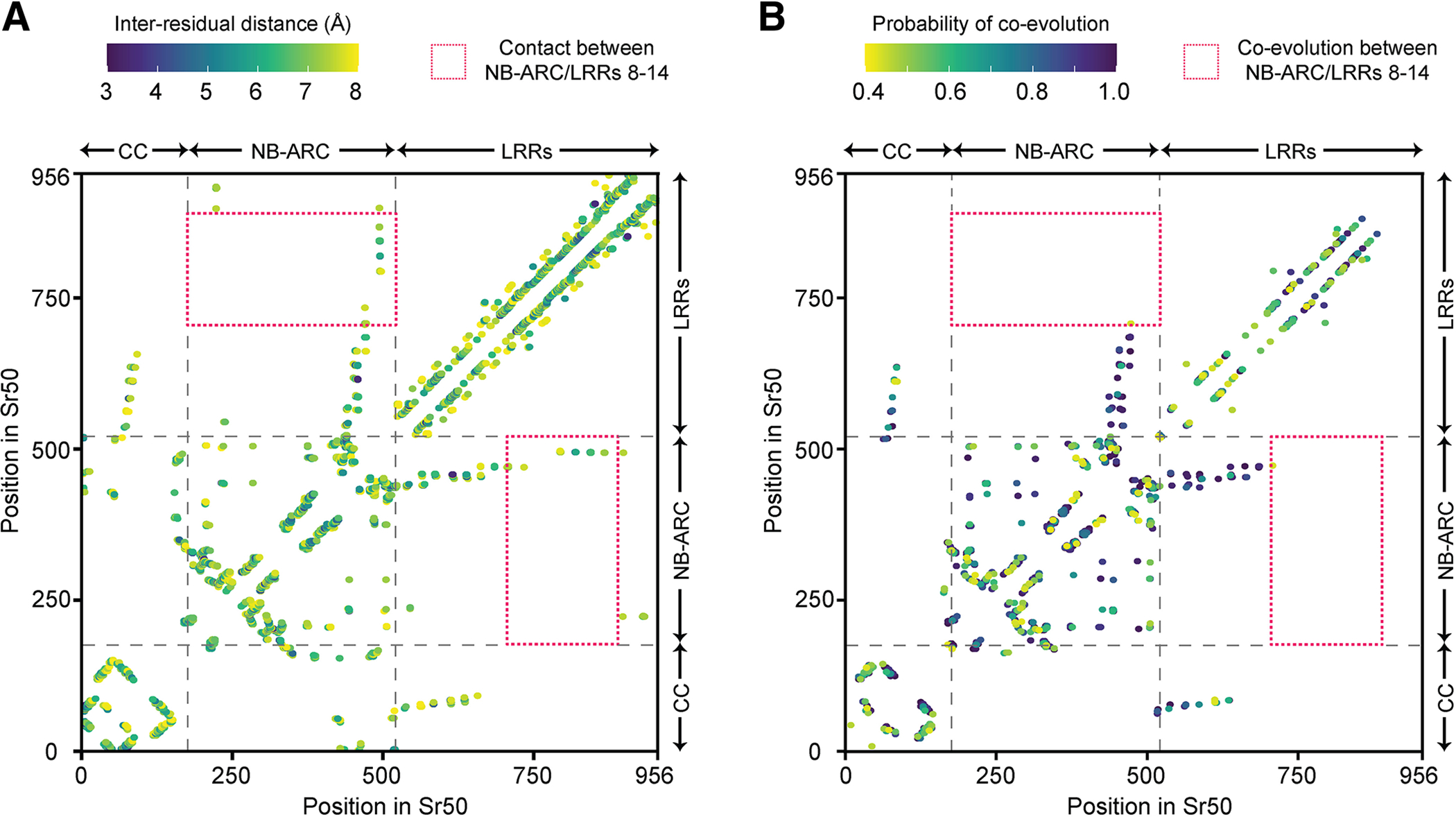
The signature of inter-residual co-evolution captured by Gremlin shows no co-evolution between nucleotide-binding (NB)-ARC and terminal leucine-rich repeats (LRRs). A, The inter-residual distances in the predicted Sr50 structure. When Cβ (Cα for glycine) atoms of two residues are within 0.8 nm, the residues are considered to be in contact. Only the long-range contact, which requires the pair of residues to be separated by at least 24 amino acids, or inter-domain contact are indicated. Multi-domain architecture (coiled coil [CC], NB-ARC, and LRRs) is provided along the axis. The red box highlights the residues of the NB-ARC domain and LRRs 8 to 14 in contact. B, The inter-residual co-evolution of NB-LRRs (NLRs) mapped to Sr50. The filtered multiple sequence alignment for Sr50 collected during structure prediction with AlphaFold2 was used to infer inter-residual co-evolution with Gremlin. The data visualized here is provided in Supplementary Table S6. Only the pairs forming long-range or inter-domain contact are indicated.
