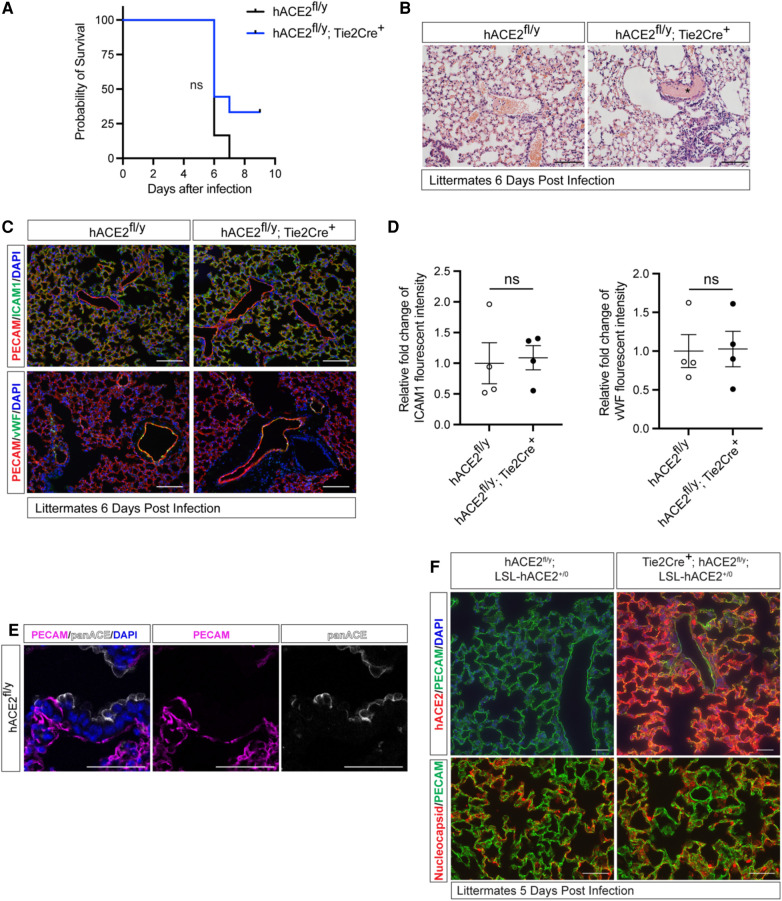
Figure 1.
Loss or gain of endothelial hACE2 does not alter SARS-CoV2 infection. (A) Survival of hACE2fl/y and hACE2fl/y; Tie2-Cre+ male mice (12 to 16-week-old males) after infection with 105 PFU of SARS-CoV-2 via intranasal administration. This viral inoculation method was used in all experiments. n = 6 (hACE2fl/y) and 9 (hACE2fl/y; Tie2-Cre+); ns, non-significant; data are from two independent experiments. (B) H&E staining of hACE2fl/y and hACE2fl/y; Tie2-Cre+ lung tissue 6 days after infection. The asterisk indicates intravascular thrombosis. Scale bars: 100 μm. (C) Immunofluorescent staining of the lung from hACE2fl/y and hACE2fl/y; Tie2-Cre+ mice with antibodies against ICAM1 or vWF (green), and PECAM (red). Images are representative of four animals per genotype. Scale bars: 100 μm. (D) Quantification of ICAM1 and vWF fluorescent intensity. The error bars represent mean ± s.d; statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired two-tailed t-test; ns, non-significant. (E) Immunofluorescent staining of hACE2fl/y lung tissue using pan-ACE2 antibodies (grey) that recognize both hACE2 and mACE2 proteins and co-stained with PECAM (magenta). Images are representative of three animals. Scale bars 50 μm. (F) Immunofluorescent staining of the lung from hACE2fl/y; LSL-hACE2+/0 and Tie2Cre+; hACE2fl/y; LSL-hACE2+/0 mice is performed using anti-hACE2 antibody or anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (red) and costained with PECAM (green) 5 days after infection with SARS-CoV-2. The hACE2fl/y allele enables these mice to be productively infected intranasally. Representative of three animals per genotype. Scale bars 100 μm.