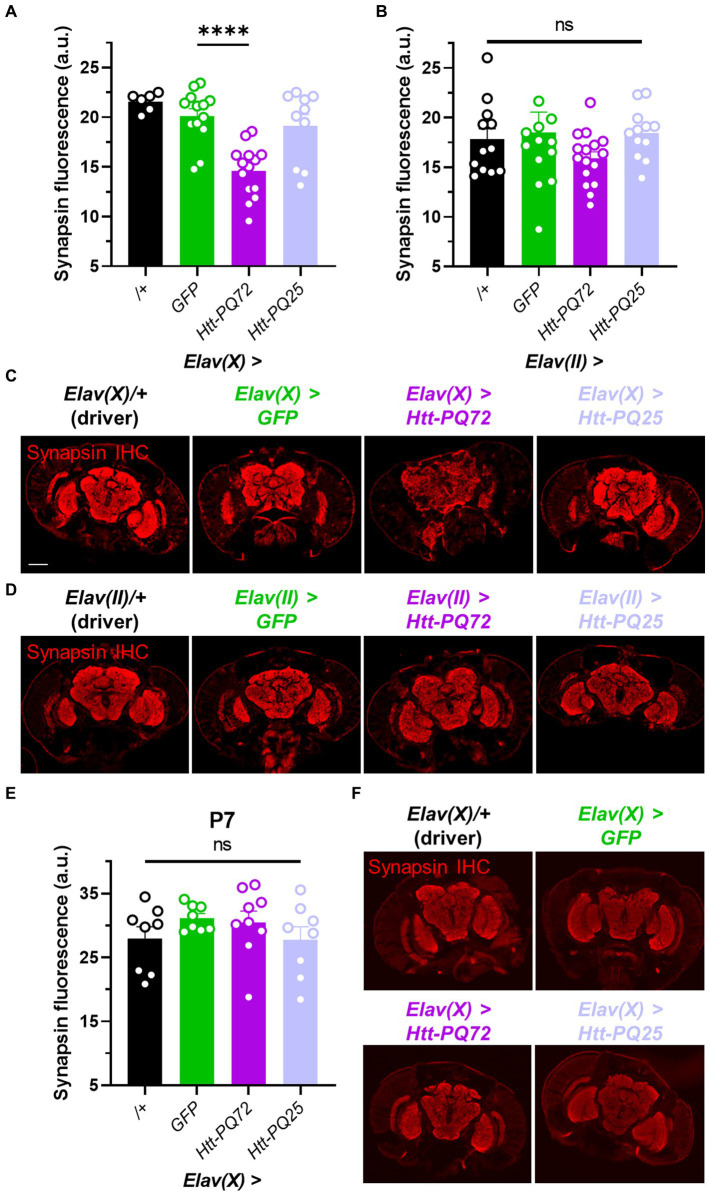
Figure 2.
Neuronal Htt-PQ72 can induce synapsin loss in the brain. (A) Quantification of synapsin staining shows a decrease of synapsin in Elav(X) > Htt-PQ72 flies at P21 (ANOVA F(3,39) = 13.6, p < 0.0001, Dunnett’s post hoc ****p < 0.0001 compared to GFP, N = 6–14 flies per group). (B) Quantification of synapsin staining shows no differences in synapsin levels in the brains of flies driven by Elav(II) at P28 (ANOVA F(3,49) = 1.1, p = 0.37, N = 12–16 flies per group). (C) Representative immunofluorescent images stained for presynaptic marker synapsin in the brain of P21 flies driven by Elav(X). Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Representative images of P28 Elav(II) fly heads stained for synapsin. (E) Quantification of synapsin staining shows no difference between any groups driven by Elav(X) at P7, when aggregates start to form (ANOVA F(3,29) = 1.0, p = 0.39, N = 8–9 flies per group). (F) Representative images of P7 Elav(X) fly heads stained for synapsin. All: Data displayed as mean ± SEM.